

浙江高考英语复习课件:专题五 语法填空 模块二 微观击破
展开
这是一份浙江高考英语复习课件:专题五 语法填空 模块二 微观击破,共60页。PPT课件主要包含了-2-,题型一,题型二,题型三,-3-,-4-,-5-,-6-,2用法 ,-7-等内容,欢迎下载使用。
模块题型二 微观击破
-2-
题型一
题型二
题型三
题型一 有提示词类(动词的时态和语态、非谓语动词、名词、形容词和副词、词性变换)考点1 动词的时态和语态命题分析时态和语态是浙江语法填空的必考点,主要考查时态语态在具体语境中的灵活运用加语境化,题干中基本不给出明显的时间状语或标志词,而是要求考生通过上下文的语境来确定时态和语态。
-3-
题型一
题型二
题型三
真题在线【典例1】(2016·全国Ⅲ)Truly elegant chopsticks might (make) of gold and silver with Chinese characters. 解析be made 考查被动语态。be made of“用……做成”,空前面用情态动词might,所以填be made。【典例2】(2016·6浙江改编)He would ask who we (be) and pretend not to know us. 解析were 考查主谓一致。句中主语是we,为复数,再结合主句中的would,根据时态一致的原则,故be动词应该用were。
-4-
题型一
题型二
题型三
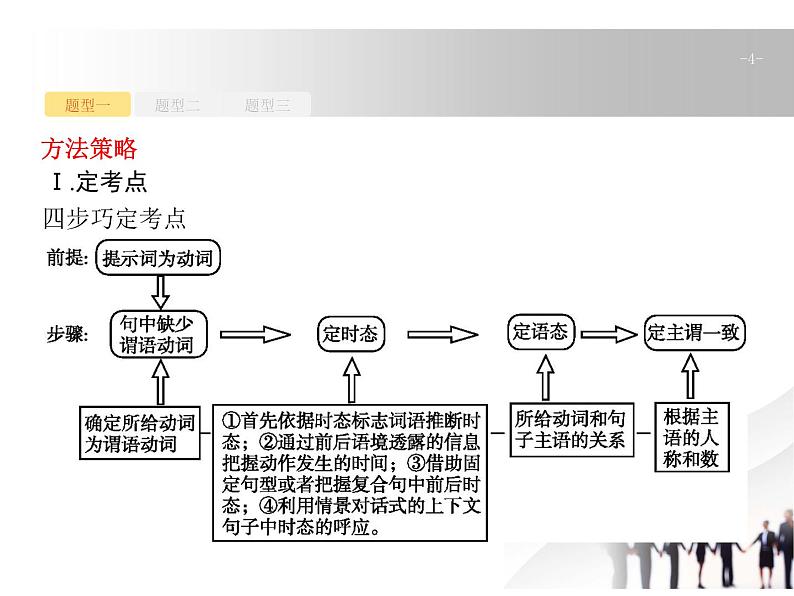
方法策略Ⅰ.定考点四步巧定考点
-5-
题型一
题型二
题型三
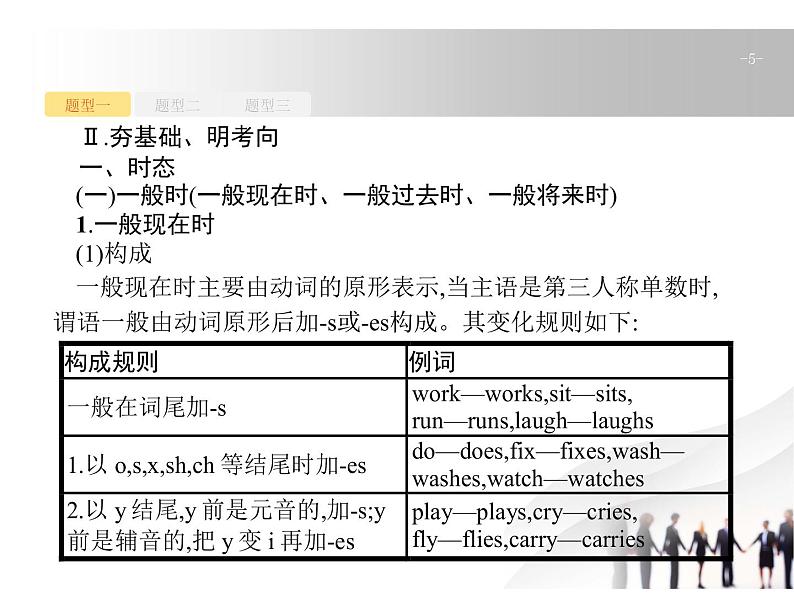
Ⅱ.夯基础、明考向一、时态(一)一般时(一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时)1.一般现在时(1)构成一般现在时主要由动词的原形表示,当主语是第三人称单数时,谓语一般由动词原形后加-s或-es构成。其变化规则如下:
-6-
题型一
题型二
题型三
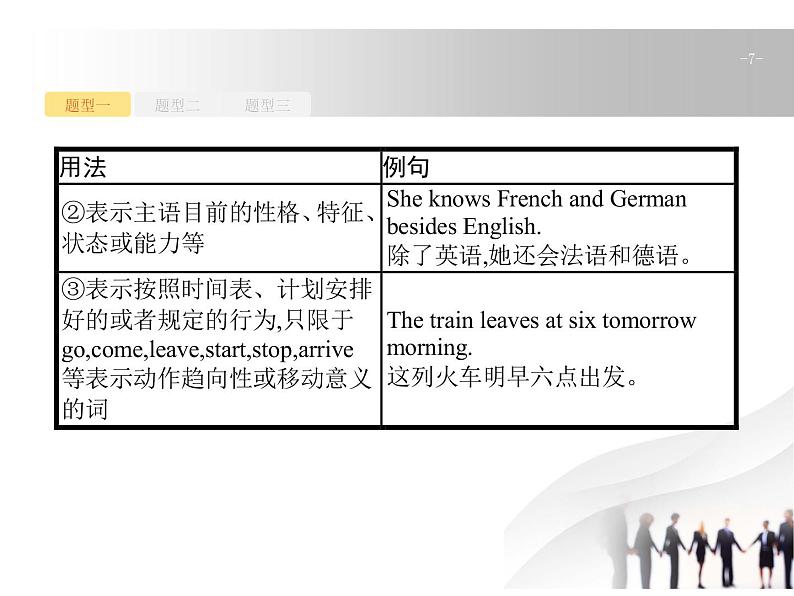
(2)用法
-7-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-8-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-9-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-10-
题型一
题型二
题型三
2.一般过去时(1)构成一般过去时由动词的过去式表示,规则动词的过去式一般由动词原形加-ed构成,其变化规则如下:
-11-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-12-
题型一
题型二
题型三
不规则动词的过去式和过去分词见附录。❋A—A—A型(现在式、过去式和过去分词同形)巧记:三式通行时,结尾是t/d。
-13-
题型一
题型二
题型三
❋A—A—Aen型(现在式和过去式同形)❋A—B—A型(现在式和过去分词同形)
-14-
题型一
题型二
题型三
❋A—B—B型(过去式和过去分词同形)①在动词原形后加一个辅音字母d或t,构成过去式或过去分词。
-15-
题型一
题型二
题型三
②把动词原形的最后一个辅音字母“d”改为“t”,构成过去式或过去分词。
-16-
题型一
题型二
题型三
③其他
-17-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-18-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-19-
题型一
题型二
题型三
❋A—B—C型(现在式、过去式和过去分词都不相同)①在动词原形后加-n或-en构成过去分词。
-20-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-21-
题型一
题型二
题型三
②ABBn(en)型过去式加-n或-en构成过去分词。
-22-
题型一
题型二
题型三
③i—a—u型变单词在重读音节中的元音字母“i”分别为“a”(过去式)和“u”(过去分词)。
-23-
题型一
题型二
题型三
④其他不规则动词的变化。
-24-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(2)用法
-25-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-26-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-27-
题型一
题型二
题型三
3.一般将来时一般将来时表示将来某一时刻的动作或状态,即单纯的将来事实。构成及用法
-28-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-29-
题型一
题型二
题型三
4.过去将来时过去将来时表示从过去某时看将要发生的动作或存在的状态。这种时态常用于宾语从句或间接引语中。
-30-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-31-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-32-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(二)进行时(现在进行时、过去进行时)1.现在进行时的用法(1)构成:现在表示此时此刻正在进行的动作,由“be+动词-ing”构成,动词-ing的构成:
-33-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(2)用法
-34-
题型一
题型二
题型三
现在进行时的其他用法:
-35-
题型一
题型二
题型三
状元笔记(1)“系动词+介词或副词”也表示进行时的意义。The bridge is under construction.桥梁正在建设中。(2)下列动词不宜用进行时:①感觉类:look,smell,feel,sound,taste,see,hear等。②感情类:like,love,prefer,admire,hate,fear等。③所有类:have,contain,own,hold,belong to等。
-36-
题型一
题型二
题型三
2.过去进行时用法:(1)过去进行时的主要用法是描述一件事发生的背景;一个动作发生的时候,另一个动作也发生。常用的时间状语有this morning,at this/that time+过去时间,all day yesterday,at...o’clock+过去时间等表示过去某一时刻、某一阶段正在进行的动作,由“was(were)+动词-ing”构成。如:He was studying in a university then.那时,他正在一所大学里学习。We were watching TV from seven to nine last night.昨天晚上七点到九点的时候我们在看电视。
-37-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(2)固定句型:be doing sth.+when...正在做某事,就在这时突然……(2017·天津)I was driving down to London when I suddenly found that I was on the wrong road.我正开车去伦敦时,突然发现走错路了。(3)表示运动和位置移动的动词可以用过去进行时表示过去将来时。这类动词主要有leave,start,arrive,go,come等。I was coming to visit you later that day,but I had to phone and cancel.我打算那天晚些时候去看你,但是不得已打电话取消了。
-38-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(三)完成时1.现在完成时(1)构成:have/has+过去分词(2)用法
-39-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-40-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-41-
题型一
题型二
题型三
状元笔记①瞬间动词可以用于现在完成时,但在肯定句中不能与表示一段时间的状语连用。在否定句中,瞬间动词可以与表示一段时间的状语连用。常用的瞬间动词有:go,come,arrive,leave,begin,borrow,buy,die,fall,stop,start,kill,close,graduate,join,finish,lose等。若瞬间动词要接表示一段时间的状语,需要做一些相应的变换,如:buy→have;borrow→keep;finish→be over;leave→be away;close→be closed;open→be open;come/go/become→be;die→be dead;fall asleep→be asleep;marry→be married;fall ill→be ill;put on→have on/wear;go to school→be a student;join the army→be a soldier/be in the army;take/get/catch a cold→have a cold
-42-
题型一
题型二
题型三
②have gone to与have been to的区别have gone to表示“到某地去了”,人可能还在路上,也可能已经到达,但一定不在说话者这里。have been to表示“去过某地”。显然是回来之后再谈论去过某地的情况。如:Mary has gone to the library.玛丽去图书馆了。(现在还没回来)Mary has been to Hong Kong.玛丽去过香港。(现在已经回来)③since只与现在完成时连用吗?since在以下情况下可以连用除完成时态外的其他时态:
-43-
题型一
题型二
题型三
●当主句表示“多长时间”时,动词可用一般现在时(当然也可用现在完成时)。如:It’s just a week since we arrived here.我们到这里才一个星期。It’s a long time since I met you last time.从上次见到你,已有很长时间了。以上各句的it is也可换成 it has been,不过在口语或非正式文体中,用一般现在时的情形比较普遍。●当主句谓语动词为seem,appear等连系动词时。It seems like years since I last saw you.从上次见到你以来好像已经有许多年了。●当主句和从句表示情况“变化”时。She doesn’t come around to see us so much since her marriage.自从结了婚,她不怎么过来看我们了。(原来经常来,结婚后就不怎么来了)
-44-
题型一
题型二
题型三
④一般过去时与现在完成时的区别He has lived in Beijing since 1995.自1995年以来他一直住在北京。(说明他现在仍在北京)He lived in Beijing before 1995.1995年前他住在北京。(现在不住在北京)
-45-
题型一
题型二
题型三
⑤现在完成时与现在完成进行时的区别①I’ve watched the film Wolf Warriors Ⅱ.我已经看过《战狼Ⅱ》了。(已经完成)②I have been watching Wolf Warriors Ⅱ these days.这些天我一直在看《战狼Ⅱ》。(仍在进行甚至仍将继续)
-46-
题型一
题型二
题型三
2.过去完成时(1)构成:have/has+过去分词(2)用法
-47-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-48-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-49-
题型一
题型二
题型三
二、语态英语中的及物动词一般都有主动语态和被动语态两种形式。被动语态由“助动词be+过去分词”构成。助动词be随着主语的人称、数和句子的时态、语气的不同而变化。
-50-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-51-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-52-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-53-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-54-
题型一
题型二
题型三
状元笔记(1)不定式符号to在被动语态中不可省略。The boss made him work overtime.→He was made to work overtime.老板让他加班。(2)“get+过去分词”也可构成被动语态,“get+married/beaten/broken/damaged/repaired/dressed”等构成的被动语态一般指动作的结果,而非动作本身。When I was cooking,I got burnt.我做饭时被烫伤了。John and Jane got married last month.约翰和简上个月结婚了。
-55-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(3)动词词组的被动语态不少短语动词相当于及物动词,可以有被动语态,但是其中的副词或介词不可遗漏。如:I was brought up in a small village.我是在一个小村子里被带大的。His new theory was laughed at by many scientists at that time.他的新理论当时遭到很多科学家的嘲笑。She was taken to the nearby hospital and was operated on immediately.她被送到附近的医院并马上动了手术。(4)介词in,on,under等+名词表示被动意义。More buildings are under construction.更多的楼房正在被修建。
-56-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(5)一些固定句式中的被动语态。It is said that...据说……It is believed that...有人相信……It is supposed that...据推测说……It is thought that...人们认为……(6)下列动词没有被动语态:①表示主语的某种属性特征或功能的词,如read,write,sell,wash,clean,cook,catch,draw,cut,photograph,peel等,常与well,badly,easily,smoothly等副词连用,用主动形式表示被动意义。The shirt doesn’t wash well.这件衬衫不好洗。
-57-
题型一
题型二
题型三
②系动词smell,taste,feel,look,sound,prove等后接形容词作表语,用主动形式表被动意义。Her voice sounds beautiful.她的嗓音听起来很美妙。一些非谓语动词以主动形式出现,表示被动意义。常见的有:be to blame,be to let(出租)等。
-58-
题型一
题型二
题型三
三、主谓一致主谓一致主要遵循三大原则:意义一致原则、语法一致原则和就近一致原则。这三个原则发生冲突时,优先考虑意义一致原则。在具体的解题过程中还要注意时态和语态。下面根据高考命题的特点具体介绍一下高考中涉及的几种情况。
-59-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-60-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-61-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-62-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-63-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-64-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-65-
题型一
题型二
题型三
状元笔记(1)从句作主语时,谓语动词一般用单数形式,但what引导的从句作主语时,谓语动词要根据从句的意义决定。What surprised me most was his attitude towards his study.最令我惊讶的是他对学习的态度。What her father left her are only some books.她父亲留给她的只有一些书。(指她父亲留给她的只有一些书,是复数概念)(2)在倒装句中谓语常与后面最接近的主语一致。In the distance was heard the clapping of hands and the shouts of the people.远处传来拍手声和人们的喊叫声。
-66-
题型一
题型二
题型三
【跳出陷阱】结构干扰结构干扰是指语法填空题中,对篇章中的某个关键词的搭配或句子结构认识不清所造成的干扰。【典例】(2016·全国Ⅲ)Confucius believed knives would remind people of killings and (be) too violent for use at the table. 解析were 不少考生可能会根据and得知应与前面的某个成分并列,是与believed并列、与would remind并列还是与killings并列?分析句子结构可知,believed后接宾语从句,宾语从句由and连接两个并列谓语。但此处描述的是过去的事实,应用一般过去时,又因主语是knives,故填were。
-67-
题型一
题型二
题型三
考点2 非谓语动词命题分析非谓语动词是语法填空的核心考点,一般不少于2个题,旨在考查考生对不同的非谓语形式的用途能否准确把握和运用。一般从以下三个角度考查:过去分词、动词-ing形式和不定式。非谓语形式在英语语言结构中功能强大,在句中除了不能作句子谓语成分之外,可作主语、宾语、定语、表语、状语或宾语补足语等成分,且可从多角度层面去进行命题。每年此考点丢分比较多。
-68-
题型一
题型二
题型三
真题在线【典例1】(2016·四川)For 25 days,she never left her baby,not even to find something (eat)! 解析to eat 考查非谓语动词。句意:25天的时间,她从不离开幼崽,甚至不去找吃的东西。此处表示未发生的动作,且所修饰的名词是动词eat的承受者。故填to eat。【典例2】(2017·6浙江)Pahlsson and her husband now think the ring probably got (sweep) into a pile of kitchen rubbish and was spread over the garden... 解析swept 考查词形变换。戒指是被冲走了,这里系动词get+过去分词,表被动。句意:Pahlsson和她丈夫现在认为,那枚戒指可能是被冲到了厨房里的垃圾堆里,然后又被倒到了花园里。
-69-
题型一
题型二
题型三
方法策略Ⅰ.定考点
-70-
题型一
题型二
题型三
Ⅱ.用技巧技巧1 理清句法功能,判断是否需要非谓语动词形式【典例】(2016·全国Ⅱ)It could be anything—gardening,cooking,music,sports—but whatever it is, (make) sure it’s a relief from daily stress rather than another thing to worry about. 解析make 考查祈使句。分析破折号后的句子结构可知,whatever引导让步状语从句,make sure...部分是主句。这里用动词原形开头构成祈使句。
-71-
题型一
题型二
题型三
技巧2 利用固定搭配,判断哪种非谓语运用(2016·全国Ⅱ)If you find something you love doing outside of the office,you’ll be less likely (bring) your work home. 解析to bring be likely to do sth.为固定结构,意为“可能做某事”。句意:如果你发现在办公室之外有喜欢做的事情,你把工作带回家的可能性就小了。
-72-
题型一
题型二
题型三
技巧3 分析非谓语动词与逻辑主语之间的关系(1)如果非谓语动词与其逻辑主语之间是主谓关系,则用动词-ing;【典例】(2016·全国Ⅲ)People probably cooked their food in large pots, (use) twigs(树枝) to remove it. 解析using 考查非谓语动词。句意:人们可能用很大的锅做饭,并用树枝来搅动。此处是动词-ing短语作状语,表示伴随状态,即主语同时发出的另一动作。(2)如果非谓语动词与其逻辑主语之间是动宾关系,则用过去分词。【典例】The producer comes regularly to collect the cameras (return)to our shop for quality problems. 解析returned 句意:生产者定期来取因质量问题而返还到我们商店的相机。动词return与名词cameras构成逻辑上的被动关系,故要用过去分词作后置定语,相当于定语从句which are returned...。
-73-
题型一
题型二
题型三
技巧4 分析非谓语动词和谓语动词发生的时间先后非谓语动词所表示的时间是一个相对时间,即相对于谓语动词的时间而言。同时也需要了解非谓语动词的不同形式所指时间的含义。如to have done,having done表示该动作在谓语动作之前发生;to be doing,doing强调与谓语动词的动作同时发生。【典例】 (spend) the past year as an exchange student in Hong Kong,Linda appears more mature than those of her age. 解析Having spent 句意:琳达作为一名交换生已经在香港度过了一年,现在看起来比那些同龄人更成熟。spend的动作发生在appears之前,Linda与spend之间是主谓关系,故用动词-ing的完成式。
-74-
题型一
题型二
题型三
Ⅲ.夯基础、明考向非谓语动词的形式及意义
-75-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-76-
题型一
题型二
题型三
一、非谓语动词作主语不定式和动词-ing作主语
-77-
题型一
题型二
题型三
状元笔记(1)动词-ing形式作主语常表示抽象的、泛指的概念;也可用it作形式主语,将真正的主语动词-ing放在句末。常用于固定句型:It’s a waste of time doing...;It’s no use/no good doing...;It is useless/nice/interesting...doing...;(2)动词-ing带逻辑主语时,只可在其前加上物主代词或名词的所有格。如:Jack’s sudden disappearing made them worried.杰克的突然失踪让他们很担心。(不可用Jack)
-78-
题型一
题型二
题型三
二、非谓语动词作表语动词-ing和过去分词作表语作表语的动词-ing和过去分词,大多数是已经形容词化的动词-ing或过去分词,而且大多数是与心理状态有联系的词。
-79-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-80-
题型一
题型二
题型三
状元笔记(1)这样的词常见的有:interesting“有趣的”,interested“感兴趣的”;exciting“令人兴奋的”,excited“感到兴奋的”;disappointing“令人失望的”,disappointed“感到失望的”等。这类动词-ing分词作表语时,一般是物作主语;而过去分词作表语时,则一般是人作主语。(2)get,become,look,seem,appear,remain等系动词后都可跟done,表示被动或主语的状态。如:remain seated/hidden,get paid/dressed/changed/stuck/hurt/injured/burnt等。This quotation from Winston Churchill tells us that we shouldn’t get discouraged right after failures.温斯顿·丘吉尔的这句名言告诉我们失败后我们不能气馁。
-81-
题型一
题型二
题型三
三、非谓语动词作定语(一)不定式作定语
-82-
题型一
题型二
题型三
状元笔记如果作定语的不定式是不及物动词,或者不定式所修饰的名词或代词是不定式动作的地点、工具等,不定式后需要加相应的介词。He has no pen to write with.他没有钢笔写字。【易错易混】如果被不定式修饰的名词为place,time,way等,不定式后的介词习惯上可以省去。It took us ages to find a place to live (in).我们花了好长时间才找到一个住处。
-83-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(二)分词作定语及物动词的分词形式作定语
-84-
题型一
题型二
题型三
状元笔记(1)分词短语作定语相当于一个定语从句,修饰前面的名词。(2)drink,learn,sink,light都有两种形式的过去分词,但作定语时,只能用拼写较长的过去分词。如:a drunken driver 喝醉酒的司机;a learned lawyer 博学的律师;a sunken ship 沉船;a lighted candle 点着的蜡烛。(3)不及物动词的分词形式作定语作定语的不及物动词的分词形式有:动词-ing和过去分词。动词-ing表示动作正在进行;过去分词只表示一个动作已完成,不表被动。
-85-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(4)动词-ing作定语时常置于被修饰词之前,用于说明被修饰词的用途、功能或目的。a walking stick拐杖a reading room阅览室
-86-
题型一
题型二
题型三
四、非谓语动词作宾语非谓语动词作宾语的主要是不定式和动词-ing。(一)只能用不定式作宾语的动词下列动词只能用不定式作宾语,请牢记下面的口诀:想要干:want,wish,hope,expect,seek,attempt,aim,claim,would like/love,desire,swear早打算:plan,prepare,arrange同意否:agree,promise,undertake,offer,choose,refuse问问看:ask,beg决定了:decide,determine,make up one’s mind,be determined尽力干:try,manage(反义词fail),struggle,strive努力做:make an effort装威胁:pretend,threaten
-87-
题型一
题型二
题型三
等发生:wait,happen付得起:affordMy English teacher promised to lend some books to me.我的英语老师答应借给我一些书。
状元笔记当非谓语动词位于but,except后作宾语时,习惯上要用不定式。并且,当其前有动词do时,则不定式不带to;若其前没有动词do,则不定式通常带to。如:We had no choice but to wait.我们除了等待之外别无选择。He never did anything but watch TV.除了看电视,他从不干任何事。It had no effect except to make him angry.除惹他生气外,没产生任何效果。I could do nothing except agree.我除了同意,没有别的办法。
-88-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(二)只能用动词-ing作宾语的动词或动词短语下列动词或动词短语只能用动词-ing作宾语,请牢记下面的口诀:考虑建议盼原谅:consider,suggest/advise,look forward to,excuse,pardon承认推迟没的想:admit,delay/put off,fancy避免错过继续练:avoid,miss,keep/keep on,practise否认完成停止赏:deny,finish,stop,enjoy/appreciate不禁介意准逃亡:can’t help,mind,allow/permit,escape不准冒险含想象:forbid,risk,include,imagine
-89-
题型一
题型二
题型三
此外,介词以及下列动词短语也要用动词-ing作宾语:be used/accustomed to,lead to,devote to,go back to,stick to,object to,get down to,pay attention to,give up,feel like,insist on,thank...for,apologize for,be busy (in),have difficulty/trouble (in),have a good/wonderful/hard time (in),spend time (in)。My mother couldn’t help smiling when she heard the good news.听到那个好消息,我妈妈情不自禁地笑起来。He was looking forward to working with the new Prime Minister.他正盼望着与新总理一起工作。The author begins his account of the tour in the forest mainly by describing various sounds.作者主要是通过描述各种声音开始叙述自己的森林之旅的。
-90-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(三)既可以接不定式也可以接动词-ing作宾语的动词或动词短语下列动词或动词短语既可以跟动词-ing作宾语,也可以跟不定式作宾语,但意义上有区别,要特别注意:go on表继续,接doing 表示做同一件事,接to do表示换一件事;regret,forget,remember,接doing 表做过,跟to do 表要去做;mean doing意味着,mean to do 打算做;try doing 试着做,try to do设法做;can’t help (to) do sth.不能帮助做某事;can’t help doing sth.情不自禁做某事I meant to give you this book today,but I forgot.我本来打算今天给你这本书的,可是我忘了。Missing this train means waiting for another hour.错过这辆火车意味着你得再等一小时。
-91-
题型一
题型二
题型三
五、非谓语动词作状语(一)不定式作状语1.不定式作目的状语不定式作目的状语,意为“为了”,可以单独放在句首、句中或句末。如果强调目的性,不定式前也可加in order或so as,但so as to不能置于句首。In order to support his family,Mr.Johnson began to plant herbs and vegetables.为了养家,约翰逊先生开始种植香草和蔬菜。Every day in our work,we are inspired by the people we meet doing extraordinary things to improve the world.在我们工作的每一天中,我们都受到那些我们遇到的、做着不平凡的事情去改善这个世界的人的鼓舞。
-92-
题型一
题型二
题型三
2.不定式作结果状语不定式作结果状语常用在下列句式中:(1)only to do表示意想不到的结果(2)enough to do足够做……(3)too...to do太……而不能……(4)so/such...as to...如此……以至于……I’m not so stupid (a fool) as to write it down.我不至于愚蠢到会把它写下来。Jane hurried back only to find that her mother had left.简匆忙赶回来却发现她的母亲已经离开了。(表示“意外或事与愿违的结果”)I’m too tired to stay up longer.我太累了,不能再熬夜了。
-93-
题型一
题型二
题型三
状元笔记only too...to结构中,too...to...并非是“太……而不能……”之意。此时,与too...to...搭配的形容词常见的有pleased,ready,willing,glad,happy等。I’m only too glad to have passed the exam.考试及格了,我非常高兴。3.不定式作原因状语形容词作表语时,后面可接不定式作原因状语,用以说明产生这种情绪的原因。用于这类结构中的形容词常见的有:happy,glad,sorry,anxious,proud,disappointed,angry,surprised,ready,delighted,pleased等。You will never know how happy I was to see her yesterday.你永远不会知道昨天看到她时,我是多么高兴。
-94-
题型一
题型二
题型三
4.在“主语+系动词+表语(形容词)+to do”结构中,句子的主语与动词不定式有逻辑上的被动关系,且形容词表示主语的特征或性质,这时,需用不定式的主动形式表示被动意义。该结构中常用的形容词有:easy,hard,difficult,important,impossible,interesting,pleasant,nice,comfortable,safe,dangerous等。This question is easy to answer.这个问题容易回答。This book is difficult to understand.这本书很难理解。
-95-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(二)分词作状语分词作状语时,可以表时间、原因、结果、条件、让步、行为方式、伴随状况等。为了强调,还可与while,when,once,if,unless等连词连用。分词作状语时其形式的选择
-96-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-97-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-98-
题型一
题型二
题型三
状元笔记某些动词的过去分词已经形容词化,且往往用于一些系表结构中,此时这些过去分词只表示一种状态,作状语时不表示被动关系,其前不用being。如:dressed in(穿着),located(坐落的,位于的),lost(迷路的),seated(坐),lost/absorbed in(沉溺于)等,不管它们作什么成分都不用其-ing形式。Absorbed in his book,he didn’t notice me enter the room.专心于读书,他没注意到我进入房间。
-99-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(三)独立成分作状语有些分词或不定式短语作状语,其形式的选择不受上下文的影响,称作独立成分。常见的有:generally speaking一般来说;frankly speaking坦白地说;judging from/by...根据……来判断;considering.../taking...into consideration考虑到……;to tell you the truth说实话;compared to/with与……相比。Judging from his accent,he is from Hong Kong.从口音判断,他是香港人。To tell you the truth,I am a little tired.说实话,我有点累。
-100-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(四)独立主格结构作状语非谓语动词作状语时,它的逻辑主语应和句子主语保持一致。但有时非谓语动词带有自己的逻辑主语,在句子中作状语,我们称之为独立主格结构。结构:(1)
-101-
题型一
题型二
题型三
My shoes removed,I entered a low-ceilinged room,treading cautiously on the soft tatami matting.(时间)我脱掉鞋子后,走进一间屋顶很低的房间,小心翼翼地踩在柔软的榻榻米垫子上。Weather permitting,they will go on an outing to the beach tomorrow.(条件)如果天气允许的话,他们将在明天组织一次海滨郊游。So many children to support,they both have to work full time.(原因)有这么多孩子要养,他们俩不得不全日工作。
-102-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(2)with+复合宾语“with+宾语+宾语补足语”结构可以构成独立主格结构。With his son so disappointing,the old man felt unhappy.由于儿子如此令人失望,老人感到很不快乐。It was a pity that the great writer died with his works unfinished.真可惜,这位伟大的作家去世时,作品尚未完成。
-103-
题型一
题型二
题型三
六、非谓语动词作宾语补足语(一)动词不定式作宾语补足语有些动词及动词短语后接不定式作宾语补足语,即“动词/动词短语+sb.+to do”。常见的这类动词或动词短语有:advise建议 allow允许 ask询问;要求beg乞求 cause导致 encourage鼓励expect期望 forbid禁止 force强迫intend意欲 invite邀请 order订购persuade说服 prefer喜爱 require需要teach教 remind提醒 tell告诉want想要 warn警告 wish想要wait for等待 depend on依靠 call on号召;要求
-104-
题型一
题型二
题型三
If we expect people to give up the habit of driving,we must give them an alternative they can rely on.如果我们期望人们放弃开车的习惯,我们必须给他们可以依赖的替代的事情。They teach kids to stand up and be themselves,and encourage them to politely decline to do things that they believe are wrong.它们(学校)教孩子们变得坚强独立,做真实的自己,并鼓励他们有礼貌地拒绝做一些他们认为错误的事情。I strongly recommend you to read it and share what you gain with me in your reply.我强烈推荐你读一读并在回信中把你的收获和我分享一下。
-105-
题型一
题型二
题型三
We were warned not to cheat again or she would need to see our parents.我们被警告不要再作弊,否则她将需要见我们的家长。状元笔记hope,welcome,agree,suggest,demand不能跟sb.to do sth.,即不能带补语。(×)hope sb.to do sth.应改为wish/expect sb.to do sth.(×)welcome sb.to do sth.应改为sb.be welcome to do sth.(×)agree sb.to do sth.应改为allow/permit sb.to do sth.(×)suggest sb.to do sth.应改为advise sb.to do sth./suggest sb.(should) do sth.(×)demand sb.to do sth.应改为require sb.to do sth./demand sb.(should) do sth.
-106-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(二)分词作宾语补足语1.过去分词作宾语补足语过去分词作宾语补足语时,句中的宾语往往就是其逻辑主语,表示被动和完成,该动词与宾语之间存在动宾关系。I’ll have my house painted tomorrow.明天我会让人把我的房子粉刷一下。
-107-
题型一
题型二
题型三
2.动词-ing作宾语补足语动词-ing作宾语补足语时,句中的宾语往往就是其逻辑主语,该动词与宾语之间存在主动关系。动词-ing作宾语补足语强调正在进行中的主动动作,即动作过程的一部分。可以带有这种复合宾语的动词有see,watch,hear,observe,feel,find,have,keep等。Recordings of angry bees are enough to send big,tough African elephants running away,a new study says.一个新的研究说:愤怒的蜜蜂的录音足以让体型巨大的、强壮的非洲大象都逃走。
-108-
题型一
题型二
题型三
状元笔记have sb.doing sth.用于否定句中,常与can’t,won’t等连用,表示“不能容忍某人做某事”。I won’t have you speaking to your dad like that.我不容许你和你父亲那样讲话。【易错清单】1.感官动词带宾语补足语的结构。结构公式(以see为例):see+宾语+do/doing/done(主动)→主语+be seen to do/doing/done结构意义:do、to do sth.表示动作的全过程或经常性动作;doing表示主动的、正在进行的动作;done表示完成的、被动的动作(如果是不及物动词则只表示完成的动作)。如:
-109-
题型一
题型二
题型三
She was seen to enter the room.她被发现进了房间。A cook will be immediately fired if he is found smoking in the kitchen.如果被发现在厨房吸烟,一个厨师将立刻被开除。The managers discussed the plan that they would like to see carried out the next year.经理们讨论了他们希望明年被执行的计划。此类动词及短语有:see,notice,watch,observe,catch(sight of),listen to,hear,feel,find等。
-110-
题型一
题型二
题型三
2.get/send 带宾语补足语的结构。(1)get/send+宾语+doing表示“使……起来”,由静止到运动并持续下去。She got her bike running very fast.她把自行车骑得飞快。(2)get+宾语+to do=let/have sb.do表示“让某人做某事”He got his brother to help him.他让他的兄弟帮助他。(3)get+宾语+done=have sth.done表示“使某事被做”He got the car started.他发动了小汽车。(4)send+宾语+to do表示“派某人去做某事”
-111-
题型一
题型二
题型三
3.make带宾语补足语的结构。使役动词make+宾语+do/done;宾语与do 为主动关系,与done是被动关系;如make 在被动语态中,to要还原。They made me repeat the story.他们让我复述这个故事。(省略to的动词不定式)He raised his voice to make himself heard.他提高了声音以便别人能听到他说话。(过去分词作宾语补足语)4.使役动词have接过去分词作宾语补足语有两种情况。(1)过去分词所表示的动作由他人完成。如:He had his money stolen.他的钱被偷了。(被别人偷去了)(2)过去分词所表示的动作由句中的主语所经历。如:He had his leg broken.他的腿断了。(自己的经历)
-112-
题型一
题型二
题型三
5.要求不定式作宾语补足语的大部分动词(have,let,notice,watch等除外)都可以作被动句中的谓语,这样,在主动句中作宾语补足语的不定式(短语)便在被动句中作主语补足语。如:The room was found to be empty.那个房间被发现是空的。(to be empty是主语补足语)The young man was considered to have great promise.这个青年被认为大有前途。(to have great promise是主语补足语)值得注意的是,作宾语补足语的不带to的不定式在被动句中作主语补足语时须带to。如:They were made to wait for hours.他们被迫等了好几个小时。
-113-
题型一
题型二
题型三
6.接动词-ing作宾语,接不定式作宾语补足语:口诀:禁止、建议和允许,接doing作宾语,接to do 作补语。forbid/advise/allow/permit doing sth.;forbid/advise/allow/permit sb.to do sth.(禁止,建议,允许某人做某事)Here’s how (keep) away from my phone for 48 hours changed me and my way of life. 解析keeping 解题时,很多考生受思维定式的影响,会想到how to do sth.“如何做某事”,但是仔细分析一下,句意应为“这里说的是远离手机48小时怎样改变了我和我的生活方式”。故应是动词-ing短语作主语,故填keeping。
-114-
题型一
题型二
题型三
考点3 形容词和副词命题分析语法填空题对形容词和副词的考查热点集中在形容词和副词的词形变化及词性转换上,以及连接副词、形容词和副词的比较等级、形容词和副词的词形转换等。真题在线【典例1】(2017·6浙江)But something made her look closer,and she noticed a (shine) object.Yes,there beneath the leafy top of one tiny carrot was her long-lost wedding ring. 解析shiny/shining 考查词形转换。作定语,修饰后面的名词object(物体),用形容词形式。
-115-
题型一
题型二
题型三
【典例2】(2014·全国Ⅰ)Finally,that hard work paid off and now the water in the river is (clean) than ever. 解析cleaner 作表语,依然用形容词,可考虑比较等级;又由“than ever”(比以前)可知,要用比较级。
-116-
题型一
题型二
题型三
方法策略Ⅰ.定考点
-117-
题型一
题型二
题型三
Ⅱ.夯基础、明考向(一)形容词1.形容词的用法
-118-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-119-
题型一
题型二
题型三
2.词性转换
-120-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-121-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-122-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-123-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-124-
题型一
题型二
题型三
3.合成形容词常见的构成
-125-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-126-
题型一
题型二
题型三
4.-ed形容词与-ing形容词-ed形容词,通常说明人,意为“(某人)感到……”;-ing形容词通常说明事物,意为“(某事物)令人……”或“令人……的(事物)”。He has a frightened look on his face.他脸上带有惊恐的神情。(他感到恐惧)He has a frightening look on his face.他脸上带着令人恐惧的神情。
-127-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-128-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-129-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-130-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(二)副词形容词加-ly变为副词的规律
-131-
题型一
题型二
题型三
状元笔记(1)以-ly结尾的形容词。如:friendly,lovely,lively,lonely,elderly等。(2)作表语时主语不能是指人的形容词。如:(in)convenient,difficult,necessary,pleasant等。
-132-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(三)形容词、副词的比较等级1.形容词和副词的比较级和最高级的构成(1)规则变化
-133-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-134-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(2)不规则变化
-135-
题型一
题型二
题型三
2.形容词、副词比较级的用法
-136-
题型一
题型二
题型三
状元笔记(1)比较级前可用a little,a bit,slightly等修饰,表示“稍微,一点儿”。It’s a little colder today than it was yesterday.今天比昨天稍冷一点儿。(2)比较级前可用much,far,a lot,a good deal,a great deal,rather等修饰,表示“……得多”。—The film is,I have to say,not a bit interesting.—Why?It’s far more interesting than the films I have ever seen.——我不得不说这部电影真的没意思。——为什么?它比我看过的所有电影都有意思。
-137-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(3)常考比较级句型①no more...than ……和……一样不……,than前后两部分在意义上都是否定的。②not more...than 不如……③no better than 和……一样;实际等于……④no less...than 和……一样;不逊于⑤more...than...与其……不如……
-138-
题型一
题型二
题型三
3.形容词、副词最高级的用法(1)形容词、副词的最高级形式主要用来表示三者或三者以上人或事物的比较,表示“最……”的意思。句子中有表示范围的词或短语。如:of the three,in our class等等。Which season do you like (the) best,spring,summer or autumn?你最喜欢哪一个季节,春天,夏天还是秋天?Among the three short girls,Mary is the tallest.在这三个矮姑娘中,玛丽是最高的。(2)“one of the+最高级+可数名词复数+比较范围”表示“……中最……之一”。Shanghai is one of the biggest cities in China.上海是中国最大的城市之一。
-139-
题型一
题型二
题型三
状元笔记(1)最高级可用by far,much,almost,nearly及序数词修饰,表示程度或顺序。The bridge being built now is by far the longest across the Yellow River.目前正在建的那座桥是横跨黄河之上的桥当中最长的。(2)most 前如不用定冠词the,就没有比较的意思,只是用来加强语气,有“很,非常”之意。I cannot do it.It’s most difficult.我干不了这件事,太难了。
-140-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(3)最高级的其他表达法①“否定词+比较级” 表达最高级含义。—Do you think that the Chinese National Games were a success?—Yes,absolutely!It couldn’t be better.——你认为这届中国全运会成功吗?——是的,绝对成功!没有比它更好的了。②比较级形式表示最高级含义。Julia is taller than any other girl in her class.=Julia is taller than all the other girls in her class.=Julia is the tallest girl in her class.朱莉娅是她班上最高的女生。
-141-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(四)连接副词★★★ 连接句子或从句的连接副词(1)表“递进”:besides,further,then,similarly,likewise,moreover,otherwise等。(2)表“结果”:therefore,consequently,accordingly,thus等。(3)其他连接副词①表示等同:similarly,equally ②表示对比:rather,oppositely③表示概括:altogether,generally ④表示列举:first(ly),second(ly),finally⑤表示条件:otherwise ⑥表示同伴关系:namely⑦表示让步:however,still,yet,nevertheless,though,anyway⑧表示时间过渡:meanwhile,sometimes,occasionally⑨表示着重特指:mainly,mostly,particularly,especially
-142-
题型一
题型二
题型三
I don’t like it;besides,it’s too expensive.我不喜欢它,而且它也太贵了。Playing on a frozen sports field sounds like a lot of fun.Isn’t it rather risky,though?在结冰的场地上玩耍听起来很有趣,然而,这难道不是太冒险了吗?【特别提醒】有的连接副词(如however等)后通常有逗号与句子的其他成分隔开。另外,有的这类副词还可位于句中或句末。He may,however,come later.不过,他也许晚一会儿就到。We all tried our best.We lost the game,however.我们都已尽了最大的努力,不过我们还是输了。
-143-
题型一
题型二
题型三
【典例1】As night fell,we became (increase) worried. 解析此题考生会误以为became与increase是系表结构,但真正的系表结构是became worried,increase的变形作为副词修饰worried,表示“日益增长地”。故填 increasingly。【典例2】There were many people waiting at the bus stop,and some of them looked very anxious and (disappoint). 解析此处考查系动词look的用法,在本空中look后接形容词。但是,考生很容易写成disappointing而造成失分,因为disappointed意为“感到失望的”,而disappointing意为“令人感到失望的”,与句子意思不相符。故填disappointed。
考点4 名词命题分析名词也是语法填空的必考点,主要考查可数名词的复数,和用所给词(所给出的动词、形容词等提示词)的名词形式填空,有时也会涉及固定搭配中的名词(不给提示词)。真题在线【典例1】(2016·6浙江改编)We can achieve a lot when we learn to let our (different) unite,rather than divide us. 解析differences 由空格前的our可知此处应用名词的复数形式。【典例2】While there are amazing stories of instant transformation,for most of us the (change) are gradual and require a lot of effort and work,like cleaning up a polluted river. 解析changes 由后面的系动词are可知,该处用复数形式。
-144-
题型一
题型二
题型三
考点1
考点2
考点3
考点4
考点5
-145-
题型一
题型二
题型三
方法策略Ⅰ.定考点
-146-
题型一
题型二
题型三
Ⅱ.夯基础、明考向一、名词的单复数
-147-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-148-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-149-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-150-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-151-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-152-
题型一
题型二
题型三
状元笔记(1)合成名词变成复数时,通常只将里面所含的主体名词变为复数,如果没有主体名词,则将最后一部分变为复数。如:sons-in-law女婿;passers-by过路人;story-tellers讲故事的人;breakfasts早餐;housewives家庭主妇。(2)第一个名词是man,woman的复合名词,两者都要变复数man teacher—men teachers(男老师)woman doctor—women doctors(女医生)男人/女人作定语修饰名词,两者都需要变复数
-153-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(3)英语中集合名词的“数”有三种情况①“形单义复”的名词:这类集合名词作主语时,谓语动词用复数。如:cattle牛;police警察;people人民(作民族、种族讲时复数为peoples);youth青年人(youths指青年们)。②“形单义单”的名词:这类集合名词作主语时,谓语动词用单数。如:baggage/luggage行李;clothing衣服;furniture家具;machinery机械;man/mankind人类。③有些集合名词作整体看时,当单数用,谓语动词用单数;作其“成员”解时,当复数用,且形式不变,谓语动词用复数。如:family家;government政府;group组;team队;class班级;audience听众。有些名词单复数同形。means,aircraft,deer,fish,Chinese,Japanese,sheep,works(工厂),cattle。
-154-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(4)有些名词如被看作整体时就用作单数,如被看作组成该集体的各个成员时就用作复数。class,family,couple,audience,government,public。
-155-
题型一
题型二
题型三
二、词性转换(形容词/动词→名词)(一)动词变名词的后缀及例词
-156-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-157-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(二)形容词变名词的后缀
-158-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-159-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(三)常表示人的后缀及例词
-160-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-161-
题型一
题型二
题型三
三、抽象名词具体化1.具有某种特性、状态、情感的抽象名词在表示具体的概念时,可以与不定冠词连用,常考到的有:
-162-
题型一
题型二
题型三
I’m disappointed the experiment turned out to be a complete failure again.我很失望,这次试验证明又一次完全失败了。2.抽象名词与a(n)连用,淡化了抽象概念,转化为似乎可以体验到的动作、行为或类别。The idea of traveling to the moon has little attraction for me.到月球上旅行的想法对我没有什么吸引力。The city’s bright lights,theatres,and movies are great attractions.城里明亮的灯,戏院,电影等有巨大的吸引力。
-163-
题型一
题型二
题型三
四、名词所有格1.名词的所有格表示所属关系,它分-’s 所有格和of所有格两种形式。Many students’ eyesight is getting poorer and poorer.很多学生的视力变得越来越差了。From the top of the hill,you can get a bird’s view of the city.从山顶上,你可以鸟瞰整个城市。
-164-
题型一
题型二
题型三
2.双重所有格双重所有格即 “of+名词’s 所有格”,表示整体中的一个或部分。用于修饰of前面的名词,即“of+名词所有格”。但此时of前面的名词一定要有a(n),two,any,some,several,no,few,another或this,that,these,those之类的修饰语(这个修饰语一般不能是one和the)。双重所有格也可由“of+名词性物主代词”构成,如:a friend of mine 我的一位朋友。指名词所有格或名词性物主代词同of构成的所有格。a play of Shakespeare’s莎士比亚的一个戏剧a friend of my wife’s我妻子的一个朋友
-165-
题型一
题型二
题型三
考点5 词形/性转换命题分析词性/形转换是语法填空的必考点之一,词性转换的方法包括派生法、转化法和合成法。牢固掌握并熟练运用构词法知识,不仅能够灵活运用到语法填空题词性转换的考查当中,还有助于提高考生对阅读中生词进行辨识的能力。真题在线【典例】(2017·6浙江)But something made her look closer,and she noticed a (shine) object. 解析shiny/shining 考查词性转换。她看到一个发光的东西。修饰名词object要用形容词形式,故填shiny/shining。
考点1
考点2
考点3
考点4
考点5
-166-
题型一
题型二
题型三
方法策略在高考备考中需要切实把握词类转换方面的相关知识,努力扩充词汇量,并要善于分析句子结构,明确充当各种成分的典型词类,那么此类题目就能迎刃而解。Ⅰ.定考点1.作主语或宾语可用名词。2.作定语、表语或补足语一般用形容词。3.修饰动词、形容词、另一个副词或整个句子一般用副词。
-167-
题型一
题型二
题型三
Ⅱ.夯基础一、派生法(一)名词见考点4;形容词和副词见考点3。(二)构成动词的前缀和后缀
-168-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-169-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(三)表示否定或相反意义的前缀、后缀及例词
-170-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-171-
题型一
题型二
题型三
二、合成法和转化法 (一)合成法合成词是由两个或两个以上的词合成一个新词的构词方式(有的合成词写在一起,有的中间需加连字符,有的是分开写的两个)。合成词的词义可以根据各个组成部分的意思加以推断。构成合成词的几个词可以是词性相同的词也可以是词性不同的词。高中阶段常见的合成形式有:
-172-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(二)转化法不增加任何成分,不改变词形,把一个单词由一种词性转化为另外一种词性的构词法叫转化法。常见的转化形式有:
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
题型二 语境提示类(无提示词)考点1 冠词命题分析冠词的考查主要集中在以下几个方面:冠词的基本用法;冠词的固定搭配或习惯用法以及抽象名词和物质名词前冠词的用法。真题在线【典例】(2017·6浙江)For Pahlsson,its return was wonder. 解析a 考查冠词。戒指的失而复得真是一个奇迹。此处wonder为可数名词,表示“奇迹,奇事”,此处为泛指,故填a。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
方法策略Ⅰ.懂规律1.下列情况很可能填 :a/an (1) +可数名词(单数); (2) +形容词+可数名词(单数) 2.下列情况下很可能填 :the (3) (+定语)+名词+ of等介词短语(表示特指); (4) (+定语)+名词+定语从句(表示特指); (5) (+定语)+名词+不定式短语或分词短语(表示特指)。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
Ⅱ.夯基础1.不定冠词的用法辅a,元an,一什么什么;可数单名前面搁。(1)在单数可数名词前,表示泛指,要想到用不定冠词。It is said that a class of 200 students attended the lecture on the nature of human beings.据说一个有着200个学生的班级参加了这个关于人类天性的讲座。(2)表示一类人或物,指同类中的任何一个,要想到用不定冠词。A doctor is a person who saves people’s lives.医生就是拯救人们生命的人。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(3)表示第一次提到某人或某物,要想到用不定冠词。I went to a nearby restaurant,but the service there was terrible.我去了附近一家饭店,但那儿的服务很糟糕。(4)在序数词前,表示“又一,再一”,要想到用不定冠词。In Guangdong Province,it is common for a building to lack a fourth floor.在广东省,楼房没有4楼是常见的事。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(5)习惯搭配all of a sudden 突然地as a matter of fact 事实上at a loss 不知所措;困惑be on a visit 参观;拜访be/go on a diet 在节食/开始节食give sb.a lift 让某人搭便车as a result 因此as a result of... 由于……have a gift for 在……方面有天赋have a good/happy time 玩得开心
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
have a word with 与……谈话in a word总之have/catch a cold 患感冒in a hurry 匆忙地in a way 从某种意义上说keep an eye on 留意;留神make a living 谋生take a walk 散步take an interest in... 对……感兴趣take/have a rest 休息一会儿to a degree在某种程度上as a whole 总体上
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
2.定冠词的用法the的用法:特指、二提、都知道,序数、唯一、与最高;一类、乐器和发明;方位习语全家找。(1)在世界上独一无二的事物、西洋乐器以及发明物的名词前要想到用定冠词。The little girl likes to play the violin and often plays it after school.这个小女孩喜欢拉小提琴,经常放学后演奏。(2)谈话双方都知道的人或物以及上文已经提到的表示人或物的名词前要想到用定冠词。We own a dog and a cat.The dog is brown,and the cat is white.我们有一只狗和一只猫。这只狗是棕色的,这只猫是白色的。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(3)序数词和形容词最高级前要想到用定冠词;As is known to all,China is the biggest developing country in the world.众所周知,中国是世界上最大的发展中国家。(4)某些形容词、分词前表示一类人或用在姓氏复数前表示一家人,要想到用定冠词。the poor穷人;the dead死者;the old老人;the aged老人;the young年轻人;the living活着的人;the weak弱者;the injured受伤的人;the strong强者;the impossible不可能的事As far as I know,the Greens are going to move to Beijing.据我所知,格林一家要搬到北京去。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(5)only,very,same,main等词修饰名词时,前面也用定冠词the。This is the only expensive dress I’ve got.这是我买的唯一一件贵的连衣裙。(6)用于“动词(hit,strike,pull,take等)+sb.+介词+the+表示身体部位的名词”结构中hit sb.on the head打某人的头hit sb.on the chin打某人的下巴pat sb.on the shoulder拍某人的肩pull sb.by the hand拉某人的手take sb.by the arm抓住某人的胳膊
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
take sb.by the hand抓住某人的手take sb.by the throat扼住某人的咽喉seize sb.by the sleeve抓住某人的袖口strike sb.in the face打某人的脸A stone hit him on the head.一块石头打到了他的头。状元笔记该结构中的the不可用物主代词代替。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(7)高频习惯搭配at the moment 此刻;目前at the same time 同时by the way 顺便说一下go to the cinema/theater 去看电影/戏剧in the distance在远处in the end最后,最终in the habit of...有……的习惯make the most/best of...充分利用……not in the least一点儿也不on the contrary相反
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
on the other hand另一方面the other day前几天;那天to tell (you) the truth (跟你)说实话to the point中肯;切题We should make the most of every minute.我们应该充分利用每一分钟。I met one of my old friends in the street the other day.那天我在大街上遇到一位老朋友。
考点2 介词命题分析语法对介词的考查以语境填词的形式为主,其考点主要集中在以下两个方面:一是介词的用法;二是介词和名词、动词以及形容词的一些高频固定搭配。真题在线【典例1】 (2016·全国Ⅲ)Chopsticks are not used everywhere in Asia.In India,for example,most people traditionally eat their hands. 解析with 句意:在亚洲并不是到处都用筷子吃饭,比如在印度,大多数人传统上用手吃饭。介词with意为“用,使用”,表示使用某种工具或人的某一功能器官,如用嘴巴、耳朵、眼睛等。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
【典例2】(2016·四川)The mother continued to care for the young panda more than two years. 解析for 句意:熊猫妈妈会继续照顾幼崽两年多。表示一段时间的名词前用介词for,故填for。【典例3】 (2016·全国Ⅱ)Most of us are more focused our tasks in the morning than we are later in the day. 解析on 考查固定搭配中的介词。be focused on为固定搭配,意为“集中于……”。故答案为on。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
方法策略Ⅰ.晓策略空格无提示词,当空格后的名词(前面一般有限定词)、代词或动词-ing在句中不是作主语、表语,也不是作动词的宾语时,那就需要填介词。具体填什么介词,要由介词与该名词的搭配及其意义来决定,也可能是由动词或形容词与介词的句式搭配来决定。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
Ⅱ.夯基础、明考向一、表示方位的介词(一)宏观图解
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(二)微观解读1.表示方位的at,in,on,to,beside/by和nearI spent an unpleasant hour at the dentist’s.我在牙医诊所度过了难熬的一小时。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
特别提醒in,on,to,off的用法in表示在某一范围之内;on表示与某一地区“毗邻,接壤”;to表示在某范围之外(不属于该范围);off表示“(时空上)离,距”。2.表示方位的between 和amongI sat down between Sue and Jane.我坐在Sue和Jane之间。The teacher was standing among the students.老师站在学生们中间。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
3.表示方位的across,through,over和past
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
二、其他高频单词的用法1.表示时间点的at,in和on
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
2.表示时间段的for和 since
3.表示交通方式的by,in和on
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
4.表示“用……”的by,in和withHe made the speech in English.他用英语发表了演讲。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(2017·6浙江)...but in order to stay she’s had to prove her language skills by taking a test which requires her to write a postcard to an imaginary friend and answer a fictional job ad.……但是为了能留下来,她得通过参加一个考试来证明自己的语言能力,这个考试需要她给一个虚拟的朋友写张明信片,和给一个虚构的招工广告写封求职信。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
5.表示“除……外”的except,except for 和besidesAll my friends took part in the party except John.His composition is good except for a few spelling mistakes.He has learned German,French besides English.
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
6.其他常考介词的用法(1)against的用法①(表示态度)反对An agreement seems to be impossible because the majority of the committee members are against it.②(表示对比)以……为背景The skier’s red clothes stood out clearly against the snow.③(表示方位)倚靠着……The girl was leaning against the wall with her arms folded.
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(2)beyond的用法①(表示位置)在……另一边,在……更远处The small village is 20 miles beyond the town.②(表示时间)晚于……He delayed the matter beyond the fixed time.③(表示程度)超出,非……所能及The book is beyond me.这本书太难了,我看不懂。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(3)over的用法①(表示方位)越过The airplane flew over the mountains and disappeared in the distance.②(表示等级或数目)高于,在……之上,超过He has got the job because he has the advantage over others of knowing many languages.③(表示时间或过程)在……期间I’m sorry I didn’t phone you,but I’ve been very busy over the past couple of weeks.
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(4)to的用法①(表示方向、距离)到,向,去It was on the way to the railway station.②(表示时间)直到……为止,到He wakes at a quarter to six every morning.③(表示比较、比例、参照)与……相比,相对于……而言I prefer oranges to apples.④达到(某一点或某个限度)Temperatures dropped to 25 degrees below zero.
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(5)with的用法①和……一起,和,同,跟Would you like to go shopping with me?②(表示同时或同一方向)随着With time going by,the little tree has grown up.③具有,带有The dictionary is what I want,but I don’t have enough money with me.
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
三、介词短语考查介词的固定搭配有两种:一是考查固定搭配中的介词;二是考查介词短语。(一)介词与动词的搭配take advantage of利用;have an effect on对……有影响;say goodbye to对……说再见;separate...from把……与……分开;make a list of列出一张……的单子;feel like想要;play with同……一起玩,玩弄;attach...to...属于,附在……上面;contribute to贡献,有助于,促成;care about关心,介意;call for需要;pay for为……付款;apply for申请;begin with以……开始;provide sb.with sth.提供某人某物;hold up举起;rely on依靠;refer to提及,参考,查阅
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(二)介词、形容词的搭配1.形容词+aboutbe anxious about 忧虑……be curious about 对……好奇be concerned about 担心……be excited about 对……感到兴奋be (un)certain about 对……(没)有把握be particular about 对……挑剔 (2017·全国Ⅰ)Feeling uncertain about his future.对他的未来感到没有把握。(2016·北京) In high school,I became curious about the computer,and built my first website.上高中的时候,我开始对电脑产生了兴趣,并建了我的第一家网站。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
2.形容词+atbe good at 擅长……be astonished at 对……吃惊be delighted at 因……而高兴3.形容词+inbe active in积极于;be absorbed in专注于;be confident in对……有信心;be dressed in穿着……;be engaged in忙于……4.形容词+forbe suitable for适合;be eager for渴望;be famous for以……著名;be fit for适合,胜任;be good for对……有益;be anxious for急切盼望,渴望
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
5.形容词+frombe free from不受……影响;be different from不同于;be absent from缺席;be far from远离6.形容词+tobe familiar to被……所熟悉;be devoted to致力于……;be harmful to对……有危害;be deaf to不愿意听;be equal to等于……;be fair to对……公平;be blind to对……是盲目的;be friendly to对……友好;be grateful to对……心存感激;be cold to对……冷淡;be kind to 对……善意;be rude to对……粗暴;be cruel to 对……残酷;be polite to 对……礼貌
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
7.形容词+ofbe afraid of害怕;be ashamed of为……感到羞耻;be aware of意识到;be capable of能够8.形容词+withby angry with(sb.)对(某人)发怒;be busy with忙于;be concerned with与……有关,涉及,关心,关注;be strict with sb.对某人要求严格;be connected with与……有关
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
常考介词短语介词与名词的常用搭配(1)at+名词,表示时间at Christmas在圣诞节;at dusk在黄昏;at dawn在黎明;at daybreak在拂晓;at midnight在午夜;at night在夜里;at noon在正午;at present目前(2)in+名词,表示方式in English用英语;in cash用现金付款;in detail详细地;in advance提前;in ink用墨水
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(3)in+名词,表示状态in debt负债;in need需要;in ruins成为废墟;in order井然有序;in comfort舒适地;in danger处于危险中;in rags穿着破烂;in peace平静地,平安地;in prison在狱中;in public公开地(4)on+名词构成的介词短语on account of因为;on behalf of代表;on condition that在……的条件下,如果……;on line在工作(或运行);on sale出售,打折;on show在展出;on the decrease在减少;on the go在忙碌中;on the increase在增加;on the way在途中;on trial在受审(5)by+名词,表示方式by accident偶然;by air/plane乘飞机;by chance偶然;by coincidence碰巧;by hand用手工;by mistake错误地;by the day按天算
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(6)of+名词,表示特征(等于相应的形容词)of benefit有益处的;of help有帮助的;of importance重要的;of significance有意义的;of use有用的(7)out of+n.表示状态out of work失业;out of danger脱离危险;out of date过期;out of touch 失去联系;out of control失去控制;out of debt不欠债;out of order出故障;out of sight看不到;out of trouble摆脱困难(2017·全国Ⅲ)It was absolutely out of control.情况完全失控了。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(8)under+n.表示被动under attack遭到袭击;under discussion在讨论中;under pressure在压力下;under repair在修理中;under the command of...在……的统帅之下;under the control of...在……控制下;under the direction of...在……指导下(2017·全国Ⅱ)When a leafy plant is under attack,it doesn’t sit quietly.当一株带叶的植物受到攻击时,它不会坐以待毙。(9)with+n.表示情绪with anger 生气地;with confidence有信心地;with delight/joy高兴地;with difficulty困难地;with pleasure乐意地;with satisfaction满意地
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(10)其他介词构成的短语①with the help of在……的帮助下;on average 平均;because of因为;next to紧挨着;instead of代替;apart from除……之外;regardless of不管,不顾②at the foot of在……脚下;at the cost of以……的代价;at the beginning of在……的开始;at the end of在……的尽头;at peace处于和平中;at war在战争中③in return作为回报;in spite of尽管;in no case 决不;in no way 决不;in addition to另外;in the face of面对;in response to作为回应(2017·全国Ⅲ)It was done with the help of the audience.它是在观众的帮助下完成的。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
跳出陷阱For those who fly to Guilin,it’s only an hour away car and offers all the scenery of the better-known city. 解析by 很多考生会纠结是根据away来选还是根据car来选,若根据away后面一般选择from,根据car前面用by构成by car。通过分析句子含义可知,此处是表示乘坐交通工具,故填by。句意:对于那些乘坐飞机去桂林的人来说,(去阳朔)只需要一个小时的车程,而且路上可以一览这座更加著名的城市(桂林)的所有景色。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
考点3 连词(并列句和从句连接词)命题分析对于连词的考查,主要涉及引导各种从句的从属连词和并列句中的并列连词。在今后高考中,连词and,but,or是考查的重点;while与when作并列连词会是高考考查的热点。倾向于要求考生分析句子成分,把握逻辑关系,填写适当的连词,以使语义通顺。真题在线【典例1】(2016·四川) It was time for her to have a new baby, it was also time for the young panda to be independent. 解析and 前后为并列关系,应用 and连接。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
【典例2】(2016·6浙江改编) Scientists have advanced many theories about why human beings cry tears,none of has been proved. 解析which 引导一个非限制性定语从句,代替先行词theories,作介词of的宾语,故填关系代词which。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
方法策略Ⅰ.定考点
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
Ⅱ.用技巧技巧1.并列连词(and,or,nor)连同类,转折(but)、因果要小心。技巧2.从句连接词:空前空后找线索 从句缺什么,补什么;主从都缺用what 技巧3.三大从句掌握好,三步判定“跑不了”三大从句包括定语从句、名词性从句和状语从句。第一步:定是否为从句当一个句子出现两个或两个以上的谓语时,而这些谓语又非并列关系,此时,我们就应该考虑是否为从句。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
确定是何种从句的三个标准:(1)逗号后面通常是非限制性定语从句【典例】(2016·全国Ⅲ)Some people think that the great Chinese scholar Confucius, lived from roughly 551 to 479 B.C.,influenced the development of chopsticks. 解析who 分析句子结构可知,空格处所在句子是非限制性定语从句。定语从句修饰先行词Confucius(孔子),且从句中缺少主语,故用who引导。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(2)及物动词或介词之后通常是宾语从句【典例】As natural architects,the Pueblo Indians figured out exactly thick the adobe walls needed to be to make the cycle work on most days. 解析how 空格后面的thick是一个形容词,填how引导宾语从句,从句作figured out的宾语。(3)系动词之后通常是表语从句【典例】(2016·北京改编)The most pleasant thing of the rainy season is one can be entirely free from dust. 解析that 分析句子结构可知,此处是表语从句,且从句中不缺任何成分,故用that引导。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
第二步:定填何类关联词填什么关联词由三大从句各自的特点决定。定语从句的引导词有关系代词和关系副词之分;名词性从句连接词分为从属连词、连接代词和连接副词。状语从句的连词也有意义和结构之分,因此,选择关联词要综合各方面因素来考虑。【跳出陷阱】Of course whenever they turned to look at him,they had to look at Mary, made her feel like a star. 解析which 考生容易受到Mary的影响,填写who为答案。如果考虑句子意义和篇章意义,我们就不难发现,本题应该填which。which引导非限制性定语从句,先行词是前面整个句子
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
Ⅲ.夯基础一、并列连词并列连词是用来连接彼此并列的词、短语、从句或句子的连词。并列连词可以分为以下五类。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
并列连词的常用句式:(1)祈使句+and/or+陈述句。当表示顺承关系时用and,表示转折关系时用or。Work hard,or you will fail.努力工作,否则你会失败。(2)when可用于并列句,意为“这时,那时”,相当于and at this/that time。常用于下列句式:①be about to do sth.when...“正要做某事,这时突然……” We were about to set off when it suddenly began to rain.我们正要出发,这时突然开始下雨了。②be on the point of doing sth.when...“正要做某事,这时突然……”
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
③be doing sth.when...“正在做某事,这时突然……” Last Monday,I was walking in the street when I suddenly saw an old man fall off his bicycle.上周一,我正在街上散步,这时突然看到一位老人从自行车上摔了下来。④had done sth.when...“刚做了某事,这时突然……” I had just finished sweeping the floor when the telephone rang.我刚刚拖完地,这时电话铃响了。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
二、状语从句(一)时间状语从句 1.表示时间的状语从句可以由when,whenever,as,while,before,until,ever since,as soon as 等词引导。They played volleyball until/till it got dark.(延续性动词)他们打排球直到天黑才结束。He didn’t go to bed until/till his father came back.(非延续性动词)直到他父亲回来他才睡觉。Please keep quiet while/when others are studying.当别人正在学习时,请保持安静。When I went into the lab,the teacher was doing an experiment.(此处 when 不能换成 while)当我走进实验室时,老师正在做实验。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
2.引导时间状语从句的其他常见连词(短语) (1)名词词组引导时间状语从句:every/each time 每一次;the moment/minute 那时(一……就……);the first/second time 第一/二次;the last time 最后一次;the day 那一天;the week 那一周等。The moment I closed my eyes,I fell asleep.我一闭上眼睛就睡着了。(2)as soon as,instantly,directly,immediately 等表示从句动作一发生,主句动作随即发生,通常意为“一……就……”,也可引导表示时间的状语从句。I had closed the door the instant I had seen the bat.我一看到蝙蝠就把门关上了。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(3)no sooner...than 和hardly...when 引导的从句表示“刚……就……”。主句中的动词一般用过去完成时,从句用一般过去时。若把no sooner,hardly 提到句首,主句须倒装。I had no sooner arrived home than the bell rung.我一到家铃就响起来了。(4)by the time引导的时间状语从句如果用一般现在时,主句则用将来完成时;从句如果用一般过去时,主句则用过去完成时。By the time we got there,the rain had stopped.到我们到达那儿时,雨已经停了。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(二)条件状语从句 1.条件状语从句由if (如果),unless (除非),in case (万一);so (as) long as (只要),on condition that/on one condition (以……为条件)等词引导。如果主句是将来时,条件状语从句要用一般现在时表示。You’ll fail the exam unless you study hard.除非你努力学习,否则你会考试不及格。As long as you don’t lose heart,you will succeed.只要你不灰心,你就会成功。2.在条件状语从句中,用一般现在时代替一般将来时,一般过去时代替过去将来时。If he is not in the office,he must be out for lunch.如果他不在办公室,那一定是出去吃午饭了。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
状元笔记在时间和条件(有时也在方式、让步等)状语从句中,主句是一般将来时,从句通常用一般现在时表示将来。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(三)让步状语从句 让步状语从句由though(although),even if(even though),no matter how/where/what...,whatever,however,whoever 等引导。Although/Though he may be troubled,he always presents a calm smiling face.尽管他可能会遇到麻烦,但他总是露出平静的微笑。While I always felt I would pass the exam,I never thought I would get an A.尽管我一直感觉我会通过这次考试,但从没想过会得一个A。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
状元笔记(1)although与though都可以与yet,still,nevertheless连用,但不能和but连用。(2)as引导让步状语从句时只能用倒装语序,即从句中的表语、状语或谓语中的实义动词置于句首,若表语是单数名词,前置时要省略冠词。Try as he may,he never succeeds.尽管他很努力,但他从未成功过。(3)whether...or.../whether...or not也可以引导让步状语从句。Whether you believe it or not,it is true.不管你相信与否,那都是真的。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(四)比较状语从句 比较状语从句由as...as,than,not so...as,the more...the more 等词引导。I have made a lot more mistakes than you have.我犯的错误比你犯的多得多。The busier he is,the happier he feels.越忙他觉得越快乐。(五)地点状语从句 地点状语从句由where,wherever,anywhere,everywhere 等词引导。You are free to go wherever you like.你愿意去哪里就去哪里。Wherever there is smoke,there is a fire.无火不生烟(无风不起浪)。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(六)方式状语从句 方式状语从句由as,just as,as if,as though 等词引导。Jack wasn’t saying anything,but the teacher smiled at him as if he had done something very clever.杰克一句话也不说,而老师却向他微笑,仿佛他做了什么聪明的事。(七)结果状语从句 结果状语从句由so that,so...that,such that,such...that 等词引导。He was so excited that he jumped from the sofa.他如此激动以至于他从沙发上跳了下来。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(八)目的状语从句 目的状语从句常由that,so that,in order that,lest (以免,以防),for fear that 等引导,放在主句之后。目的状语从句常用情态动词may(might),can (could)等。lest,for fear that 后面常用“(should)+动词原形”的虚拟语气。Besides,I will tell him what you look like so that you can find each other easily.另外,我会告诉他你长什么样,以便你们能容易地找到对方。(九)原因状语从句原因状语从句由because,since,as引导。Since everyone is here,now let’s begin.大家都到齐了,现在开始。He had to stay at home yesterday because he was ill.昨天他必须待在家里,因为他病了。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
三、定语从句定语从句是在主从复合句中,对某一名词或代词起修饰作用的从句。被修饰的名词或代词叫先行词,引导定语从句的词叫关系词。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(一)关系代词引导的定语从句1.who,whom,whose引导的定语从句(1)who或whom均可指代人,但who在从句中作主语或宾语,whom在从句中作宾语;两者在引导限制性定语从句时常可用that替换。作主语时,who/that不可省略;作宾语时,whom/who/that可以省略。I’ve become good friends with several of the students in my school who/whom/that I met in the English speech contest last year.我与好几位去年在英语演讲比赛中结识的同校同学成了好朋友。Happiness and success often come to those who are good at recognizing their own strengths.幸福与成功通常降临到那些擅于认识到自己的长处的人身上。I have many friends to whom I’m going to send post cards.我有很多我打算给寄贺卡的朋友。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(2)whose表所属关系,一般指人,也可指物,在从句中作定语。指物时相当于of which;指人时相当于of whom。I paid a visit to a school nearby whose environment was very beautiful.我参观了附近的一所学校,它的环境非常优美。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
2.that,which引导的定语从句(1)which指物,在从句中可以作主语、宾语,也可作定语,作宾语时可以省略。that指人或物均可,在从句中可以作主语、宾语、表语,作宾语时可以省略。We’ll reach the sales targets in a month which we set at the beginning of the year.我们一个月内就可以达到年初设定的销售目标了。Every day I practiced reading and writing,which I used to avoid as much as possible.每天我都练习过去尽量避免去做的阅读和写作。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(2)限制性定语从句中,关系代词只用that不用which的情况:·先行词为不定代词anything,nothing,something,everything,all,some,none,little,few,the one等时。I refuse to accept the blame for something that was someone else’s fault.我拒绝接受因别人的错误而对我进行的指责。·先行词是形容词最高级或序数词,或先行词前有形容词最高级或序数词修饰时。The first place that they visited in Guilin was Elephant Trunk Hill.他们在桂林参观的第一个地方是象鼻山。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
·先行词被the only,the very,the last,the same,any,every,each,few,little,no,some,all等修饰时。The only part of the meal that I really liked was the dessert.这顿饭只有甜点是我真正爱吃的。·先行词中既有表示人又有表示物的名词时。They will never forget the things and persons that they’ve seen or heard of during their long journey.他们将永远不会忘记在他们的长途旅行中见到或听说过的人和事。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(3)关系代词只用which而不用that的情况:·关系词引导非限制性定语从句时。In ten years,I will build up my own firm,which can help many people solve the problem of finding a job.十年后,我将建立自己的公司,这能帮助很多人解决就业的问题。·关系代词前有介词时。We live in an age in which more information is available with greater ease than ever before.我们生活在一个比以前更容易获得信息的时代。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
3.as引导的定语从句·as可以引导限制性定语从句,常用于“so/such/the same+先行词+as...”结构中。Such machines as are used in our workshop are made in China.像在我们车间使用的机器是在中国制造的。·as也可以引导非限制性定语从句,定语从句说明整个句子,可放在主句之前、之中或之后。常用的这种类似插入语的句式有:as the saying goes,as is said above,as is mentioned above,as often happens,as is often the case,as is reported in the newspaper等。As is known to us all,if we are in trouble,it is not our phones but our friends that can really help us out.众所周知,当我们处于困境中时,不是我们的手机而是我们的朋友能真正帮我们摆脱困境。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(二)关系副词(when/where/why)引导的限制性定语从句1.where引导的定语从句where(=in/at/on/which)表示地点,在定语从句中作地点状语,其先行词往往是表示地点、场合的名词,如place,room,house,school,hotel,factory,street,town,city,country等。The village where I was born has grown into a town.我出生的那个村庄已经变成了一个城镇。状元笔记当先行词为situation,case,stage,point,activity,atmosphere等抽象名词,且引导词在定语从句中表示事情发生的情况、阶段等时,常用关系副词where引导。Students should involve themselves in community activities where they can gain experience for growth.学生应该参与社区活动,他们能从活动中获取成长的经验。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
2.when引导的定语从句when(=at/in/on/during +which)表示时间,在定语从句中作时间状语,其先行词常常是表示时间的名词,如time,day,year,hour等。I am looking forward to the day when my daughter can read this book and know my feelings for her.我一直盼望着这一天,我女儿能读到这本书并了解我对她的情感。3.why引导的定语从句why(=for which)表示原因,在定语从句中作原因状语,其先行词一般是reason。He didn’t give the reason why (=for which) he came so early.他没有说明自己来这么早的原因。状元笔记非限制性定语从句中,用for which表示原因而不用why。I had told them the reason,for which I didn’t attend the meeting.我把理由告诉了他们,为此我没有去开会。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(三)介词+关系代词引导的定语从句 在“介词+关系代词”引导的定语从句中,关系代词只能用which或whom。先行词指物时,用which;先行词指人时,用whom。在这个结构中,介词和关系代词的确定:1.根据从句中谓语动词的搭配习惯。I will work hard to enter Beijing University,from which Tu Youyou graduated.我将努力学习,力争考上屠呦呦毕业的北京大学。2.看与从句中形容词的搭配。The student with whom she is strict has made great progress.她要求很严的那位学生取得了很大进步。这就是我花10元钱买的那本书。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
3.根据先行词的搭配习惯。The company in which Peter is working is very famous.彼得所在的公司非常出名。4.句子的意思。I wish to thank Professor Smith,without whose help I would never have gone this far.我希望感谢史密斯教授,没有他的帮助,我永远不会走这么远。5.表“所有”关系或“整体中的一部分”时,用of。在some,any,few,little,none,all,both,neither,many,most,each等代词或数词的前、后表示整体与部分的关系可以用of which/whom。Maria has written two novels,both of which have been made into television series.玛丽亚已经写了两部小说,它们都被拍摄成电视连续剧了。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(四)两种特殊的定语从句1.分隔式定语从句 分隔式定语从句是指先行词与关系代(副)词分隔。Great changes around us take place before our eyes every day which we pay little attention to.(先行词great changes与定语从句which we pay little attention to分隔) 我们很少关注眼前在我们周边每天发生的巨大变化。2.插入式定语从句 插入式定语从句是指关系代词与从句之间有插入语。We must believe in ourselves,which,in my opinion,is the most important in our life.(关系代词which与从句其他成分之间有插入语in my opinion) 我们必须相信我们自己,在我看来,是我们生活中最重要的。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
误区警示有些考生在分析句子时,一看见逗号就以为一定要用which而不用that,但有时该句根本就不是定语从句。①If a book is in English,that means slow progress for you.(句中已有if引导的状语从句,逗号后为主句,that为主句主语。) ②I don’t doubt,in any case,that our school team will win the game.(该句中in any case是插入语,that引导的是宾语从句,作动词doubt的宾语。) 名师指津定语从句解题方法:关系词的选择1.先看先行词,确定人或物2.分析定语从句中的句子成分3.确定关系代词的人称和数4.注意that和which的特殊情况
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
四、名词性从句名词性从句指的是在复合句中起名词作用的从句,共有以下几类:主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句和同位语从句。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(一)主语从句1.引导主语从句的连接词:从属连词that,whether/if;连接代词what,who,whom,whose,whatever,whichever,whoever等;连接副词when,where,why,how,whenever等。What I want to stress is that you should make it a rule to practice speaking Mandarin.我想强调的是你应该养成练习说普通话的习惯。When the delayed flight will take off depends much on the weather.延迟的飞机何时起飞在很大程度上取决于天气。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
2.主语从句一般放在句首,但有时也可用it作形式主语,而将主语从句移到句子的末尾。常见的句型:(1)It+be+形容词(necessary/important/likely/uncertain等)+that从句It isn’t likely that I should accept such an offer as that.我不可能接受像那样的帮助。(2)It+be+名词词组(no wonder,an honor,a good thing,a pity,no surprise等)+that从句。It’s no surprise that our team has won the game.我们队获胜一点都不令人吃惊。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(3)It+动词/动词短语(seem,appear,happen,matter,turn out,occur to,make no difference等)+that从句。It suddenly occurred to her that Joe was afraid of being alone.她突然想到乔害怕独自一个人待着。(4)It+be+过去分词(said/reported/decided/believed等)+that从句It is said that Mr.Green has arrived in Beijing.据说格林先生已经到了北京。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(二)宾语从句1.引导宾语从句的连接词:从属连词that,whether,if;连接代词what,who,whose,whatever,whichever,whoever等;连接副词when,where,why,how等;从句用陈述语序。 (2016·浙江)Nobody entering a university knows exactly what they want to study.进入大学的人中,没有人确切知道他们想学什么。We promise whoever attends the party a chance to have a photo taken with the movie star.我们许诺,任何参加这个聚会的人都有跟那个电影明星合影的机会。 I learned from your post that you want to improve your Mandarin.在帖子上我得知你想提高你的普通话水平。We must find out when Karl is coming,so we can book a room for him.我们必须弄清楚卡尔什么时候来,以便我们可以为他预订房间。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
2.it作形式宾语的宾语从句(1)一些动词后的宾语从句有宾语补足语时,则需要用it作形式宾语,而将that引导的宾语从句后置。常见的这类动词有:find,feel,think,consider,believe,guess,suppose,make等。I think it necessary that we take plenty of boiled water every day.我认为我们每天喝大量的开水是有必要的。(2)动词appreciate,hate,like,dislike,enjoy等表示“喜欢”“厌恶”的动词以及一些动词短语see to,depend on,rely on等常用it作形式宾语,而将宾语从句后置。I’d appreciate it if you would like to teach me how to use the computer.如果你愿意教我如何使用电脑,我会感激不尽。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
状元笔记(1)doubt作“怀疑”解,后接宾语从句时,如主句是肯定句,宾语从句用 whether 或 if 引导;如主句是否定句或疑问句,宾语从句只能用 that 引导。I doubt whether/if he is fit for the job.我怀疑他是否能胜任这份工作。I don’t doubt that he can do it very well.他能把它做好,我不怀疑。(2)否定前移(若主句主语为第一人称,且谓语动词为 think,consider,suppose,believe,expect,fancy,guess,imagine 等,其后的宾语从句若含有否定意义,一般要把否定词转移到主句谓语上,从句谓语用肯定式。)I don’t think this dress fits you well.我认为这件衣服不适合你穿。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(三)表语从句表语从句是在复合句中作表语的名词性从句,放在系动词之后,一般结构是“主语+连系动词+表语从句”。可以接表语从句的连系动词有 be,look,remain,seem 等。1.引导表语从句的连接词:从属连词that,whether;连接代词what,who,whose,whatever,whichever,whoever等;连接副词when,where,why,how等;从句用陈述语序。This is where our problem lies.这就是我们的问题所在。That’s just what I want.那正是我想要的。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
The question is whether we can make good preparation in such a short time.问题是我们是否可以在如此短的时间内做好准备。From him,I realize the secret to success is not where you were born,but what you are doing in your life.从他身上,我意识到成功的秘诀不在于你生于何处,而在于在生活中你在做什么。2.as if/as though引导的表语从句as if/as though引导的表语从句常跟在be动词seem,look,taste,sound,feel,appear等动词之后。The thick smog covered the whole city.It was as if a great black blanket had been thrown over it.浓雾覆盖着整座城市,好像把一个巨大的黑色的毯子扔到它的上面。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
3.because,why引导的表语从句because,why也可引导表语从句,但because引导的表语从句,主语不能是reason或cause(该结构常用that引导)。常用于以下句型:The reason why he is late for school is that he missed the early bus.他上学迟到的原因是他错过了早班车。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
状元笔记(1)what与that在引导名词性从句时的区别what引导主语从句时在从句中充当句子成分,如主语、宾语、表语,而that引导从句,不充当成分。What you said yesterday is right.你昨天说的是对的。(what引导主语从句,作said的宾语) That she is still alive is a consolation.她还活着真是一件令人慰藉的事情。(that引导主语从句,不作任何成分,但不可省略)
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(2) whether,if(是否)引导名词性从句的区别在下列情况下一般只能用whether,不用if:①引导主语从句并在句首时;Whether he will be able to come tomorrow remains a question.他明天是否能来仍然是个问题。②引导表语从句时;③引导从句作介词宾语时;④从句后有“or not”时;
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
It remains to be seen whether or not this idea can be put into practice.这一想法能否付诸实践还有待观察。⑤后接动词不定式时。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
(四)同位语从句同位语从句在句中作某一名词的同位语,位于该名词之后,用以说明该名词的具体内容。1.常见的后跟同位语从句的名词有:fact 事实 conclusion 结论demand 要求 doubt 怀疑advice 建议 hope 希望idea 主意 information 信息message 消息 news 消息order 命令 possibility 可能性promise 诺言 question 问题request 请求 suggestion 建议thought 想法 plan 计划
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
There is no denying the fact that the environment is getting polluted more and more seriously.不可否认,环境污染越来越严重了。The manager put forward a suggestion that we should have an assistant.There is too much work to do.经理提出了我们应当有一位助手的建议。我们要做的事情太多了。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
2.引导同位语从句的连接词有:that,whether,how,where,when,why等。Where did you get the idea that I could not come?你在哪儿听说我不能来?I have no idea when he will come back home.我不知道他什么时候回家。The problem whether we should continue to do the experiment hasn’t been solved.我们是否应该继续做实验这一问题还没解决。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
状元笔记(1)在同位语从句中,that,whether不作句子成分。that无实义,whether意为“是否”,if一般不引导同位语从句。引导同位语从句的连接词一般都不能省略。(2)引导名词性从句时,that没有词义,在从句中不作任何成分。当从句意义完整,不缺任何成分时,往往选用that;而what引导名词性从句时,意为“什么”或“……的”,在从句中用来作主语、表语或宾语。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
状元笔记1.高分三步曲(1)若两个句子(有两个主谓结构)之间没有句点或分号,也没有连词,那空格处通常是填连接词,否则,句子结构就不完整。(2)根据两句之间的意义和逻辑关系,或者根据句式结构,确定是并列句还是某种主从复合句。(3)一旦判断是名词性从句,就根据名词性从句中缺少什么句子成分来确定选用什么连接词,若从句中缺少主语、宾语或表语时,用连接代词,若作状语就用连接副词;如果不缺少成分则要考虑意思是否完整,是否需要用whether/if;如果不缺少成分且意思完整用that。
题型一
题型二
题型三
-3-
2.同位语从句与定语从句的区别同位语从句是对前面名词的内容作进一步的解释、说明,引导词只起引导作用,不在句中作任何成分,一般不可省略。定语从句是对前面名词进行修饰、限制,引导词在句中作一定的句子成分。The news that they had won the game soon spread over the whole school.他们赢得比赛的消息很快就传遍了整个学校。(同位语从句,进一步解释news的内容) The news that you told me yesterday was really disappointing.你昨天告诉我的消息真的很令人失望。(定语从句,修饰news)
-271-
题型一
题型二
题型三
题型三 代词命题分析高考重点考查人称代词、物主代词及反身代词的用法,不定代词以及it的用法。试题的设计注重语境设置,要求考生将句子意思和句子结构联系起来选出正确的代词。真题在线【典例1】(2017·6浙江)“She thought I had hurt (I),”says Pahlsson. 解析myself 强调主语I,作动词hurt的宾语,用反身代词。
-272-
题型一
题型二
题型三
【典例2】(2015·全国Ⅰ)A few hours before,I’d been at home in Hong Kong,with (it) choking smog. 解析its 空后为动词-ing词组choking smog,设空处作定语,故应填形容词性物主代词its。句意:几个小时前我还在香港的家中,呼吸着那里令人窒息的烟雾。【典例3】Raise your leg and let stay in the air for seconds. 解析it 根据语境可知let的宾语为前文提及的your leg,故用it替代,以避免重复。句意为:抬起你的一条腿并让它悬空几秒钟。
-273-
题型一
题型二
题型三
方法策略
-274-
题型一
题型二
题型三
代词(一)人称代词人称代词的主格和宾格在句中作不同的成分,主格多作句子主语,有时用作表语;宾格用在及物动词或介词后作宾语,也可作表语或同位语。在口语中,常用人称代词的宾格作表语。
-275-
题型一
题型二
题型三
Thank you for your letter.谢谢你的来信。I bought a present for him.我给他买了件礼物。To really understand a man we must judge him in misfortune.—Napoleon(主格we作主语;宾格him作宾语)只有在不幸时才能真正了解一个人。——拿破仑状元笔记介词后面只能跟人称代词的宾格作宾语,不能接主格。There is a desk between you and I.(误)There is a desk between you and me.(正)你和我之间有张桌子。
-276-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(二)物主代词形容词性物主代词置于名词之前,起修饰作用,表示“……的”,在句中作定语。名词性物主代词相当于“形容词性物主代词 + 名词”,在句中作主语、表语或宾语。The main difference between our brains and those of monkeys is that ours are bigger.我们的大脑和猴子的大脑的主要差别在于我们的要大些。(our作定语,修饰名词brains;ours作主语,相当于our brains)
-277-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(三)反身代词反身代词是由第一、二人称的形容词性物主代词或第三人称的人称代词宾格加词缀-self或-selves构成。
-278-
题型一
题型二
题型三
1.反身代词的基本用法
-279-
题型一
题型二
题型三
2.反身代词的习惯用法(1)与介词连用by oneself独自地;of oneself自动地;for oneself为自己(2)与动词连用devote oneself to致力于;dress oneself自己穿衣;enjoy oneself过得愉快;boast oneself自夸;help oneself to随便吃,随便用;hide oneself把自己藏起来;make yourself at home不拘束;say to oneself心里想;seat oneself坐下;teach oneself自学;come to oneself苏醒;behave oneself表现得体,有礼貌;apply oneself致力于……。
-280-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(四)不定代词1.either,both,neither,all,any,none的区别
-281-
题型一
题型二
题型三
Both men and women are living longer these days in industrialized countries.在工业化国家,现在男性和女性都会活得更长。2.one,another,the other,some,others,the others的区别There are two pens here.One is his,the other is Tom’s.这儿有两支钢笔,一支是他的,另一支是汤姆的。
-282-
题型一
题型二
题型三
Some like staying at home at the weekend;others like going to the cinema.一些人喜欢周末待在家里,另一些人喜欢去看电影。I don’t like this book.Please give me another one.我不喜欢这本书,请再给我一本。
-283-
题型一
题型二
题型三
3.none,nobody,nothing
-284-
题型一
题型二
题型三
If I had some money,I would lend him some,but unfortunately,I have none.如果我有钱的话,我就借给他一些了,但遗憾的是,我没钱。Nothing can stop him going there.没有什么事能阻止他去那里。
-285-
题型一
题型二
题型三
4.many,much,few,little,a few,a little的区别
-286-
题型一
题型二
题型三
注意:only a few=few;only a little=little;quite a few=many;quite a little=much(2016·浙江)A scientist working at her lab bench and a six-month-old baby playing with his food might seem to have little in common.一位在她的实验台工作的科学家和一个六个月大的玩弄食物的孩子似乎没有共同之处。
-287-
题型一
题型二
题型三
5.one,ones,the one,the ones,that,those的区别
-288-
题型一
题型二
题型三
We have various summer camps for your holidays.You can choose one (=a summer camp)based on your own interests.我们为您的假期提供了各种各样的夏令营,您可以根据自己的兴趣选择一种。(one代替“a/an+单数名词”)These yellow waistcoats are so small.I want those green ones.这些黄色的马甲太小了,我想要那些绿色的。The climate of Guangzhou is much better than that of Xi’an.广州的气候比西安的好多了。The students in our class work harder than those in their class.我们班的学生比他们班的更努力。
-289-
题型一
题型二
题型三
Mr.Zhang gave me a very valuable present,one that I have never seen.张先生给了我一件非常有价值的礼物——一件我从来没有见过的礼物。One has to take care of oneself and one’s family if he can.如果可能的话,一个人必须照料自己和家人。
-290-
题型一
题型二
题型三
6.it的用法 (1)指代时间、天气和距离。It is rainy in spring in China.中国春季雨水多。(2)指代提到过的或正在谈论的动物或事物,及已知或正在发生的事实或情况等。The employment rate has continued to rise in big cities thanks to the efforts of the local governments.由于当地政府的努力,大城市的就业率不断上升。(3)指代动物、性别不详的婴儿或猜测中不确定的人。What a beautiful baby!Is it a boy?多漂亮的孩子啊!是男孩儿吗?
-291-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(4)用于某些句型。It’s time for sth.该做某事了。It’s time to do sth.到做某事的时候了。It’s time for sb.to do sth.某人该做某事了。It’s (about/high) time+that从句 某人该做某事了。(从句谓语用过去式或“should+动词原形”,should不可省略)It’s the first (second...) time+that从句 某人第几次做某事。(从句谓语用现在完成时)It’s+时间段+since从句 自从……有一段时间了。
-292-
题型一
题型二
题型三
(5)用作形式主语或形式宾语,代替不定式、动名词或从句。(具体句型结构见名词性从句部分)It is important that we should learn English well.学好英语很重要。I’d appreciate it if you could attend our party.如果你能参加我们的聚会,我将不胜感激。(6)it构成强调句it引导的强调句,通常形式为:It+be+被强调部分+that/who+其他。这种强调句由普通陈述句转换而来,用来强调句子的主语、宾语或状语。Karl bought Marva a bicycle on her birthday.→It was Karl that/who bought Marva a bicycle on her birthday.(强调主语)
-293-
题型一
题型二
题型三
状元笔记强调句中的that/who与定语从句。It was the student that/who asked the silly question.(强调句)是这个学生问了这么一个愚蠢的问题。He was the student who asked the silly question.(定语从句)他就是那个问了愚蠢问题的学生。
相关课件
这是一份2024届高考英语一轮总复习第三部分专题五语法填空课件,共6页。PPT课件主要包含了题型要求,命题分析等内容,欢迎下载使用。
这是一份2024年高考英语一轮复习专题五语法填空课件,共6页。PPT课件主要包含了题型要求,命题分析等内容,欢迎下载使用。
这是一份2022版高考英语二轮复习 模块2 语法知识 专题1 语法填空课件,共31页。PPT课件主要包含了专题一 语法填空,考情分析·明方向,一考情归纳,掌握攻略·巧破题,实战导引·点迷津等内容,欢迎下载使用。