






高中物理人教版 (新课标)选修32 库仑定律课堂教学ppt课件
展开
这是一份高中物理人教版 (新课标)选修32 库仑定律课堂教学ppt课件,共60页。PPT课件主要包含了1库仑定律,2电场强度,3高斯定理,国际单位制中,静电力的叠加原理,解由库仑定律,由万有引力定律,电场和电场强度,电场的重要特征,电场强度场强等内容,欢迎下载使用。
8.4 静电场的环路定理、电势
8.5 导体静电平衡 电容器
8.6 稳恒电流、基尔霍夫定律
• 电荷有两类;同类电荷相互排斥,异类电荷相互吸引。
• 电荷的量子化:任何带电体所带的电量只能 是电子电量e 的整数倍,即Q = ne ( n是整数)。
• 库仑定律:在真空中两个点电荷之间的相互作用力的大小与它们之间所带的电荷量的乘积成正比,与它们之间的距离平方成反比;作用力的方向沿着它们之间的连线;同号电荷相互排斥, 异号电荷相互吸引。
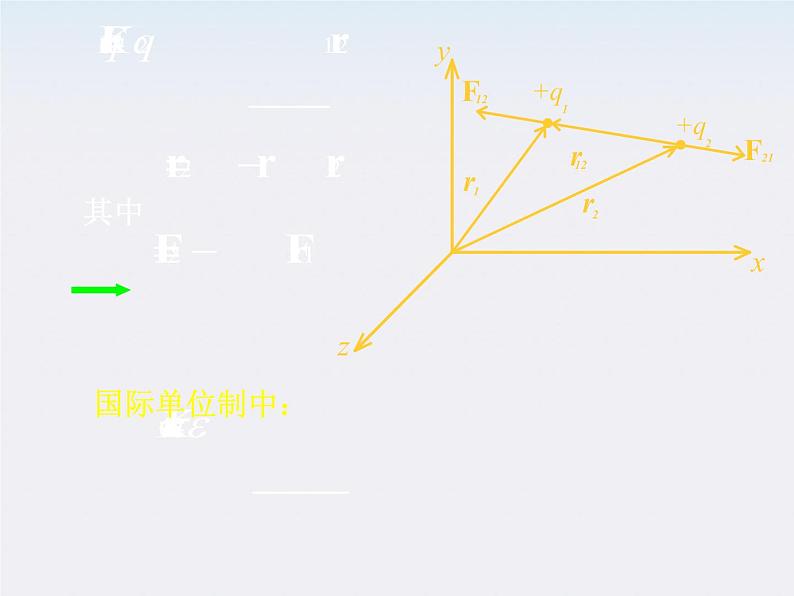
有n 个点电荷q1 , q2 ,…, qn , 其中任一个电荷
qi 所受的静电力为
真空电容率(真空介电常数):
库仑2/(牛顿·米2)
Quick quiz 1
[例] 氢原子中电子和质子的距离约为5.310-11 m , 求两者之间的静电力和万有引力的大小。
静电力远大于万有引力定律:1039 倍
电场 1. 电荷 电场 电荷
对处在电场中的其他电荷有力的作用。
2.近代物理证明:电场是一种特殊物质。
它具有能量、动量和质量。真空中可以存在电场。
4.静电场:相对观察者静止的电荷所产生的电场。
电场中某点的电场强度E 等于单位正电荷在该点所受的电场力。
点电荷q(源电荷)产生的场强为:
点电荷系在某点所产生的场强等于各点电荷单 独存在时在该点所产生的电场强度的矢量和 — 场强叠加原理
电荷连续分布时,可用积分求场强
[例] 两等量异号电荷+q和-q,相隔一定的距离l,当考察点离开两点电荷比较远时,两电荷体系的特征可用特征向量 表示,这样的两电荷系统称为电偶极子。 的方向由负电荷指向正电荷,称为电偶极子的臂或轴;P称为电偶极矩,简称电矩。试计算电偶极子的臂的延长线上和中垂线上的场强分布。
[解] (1) 求电偶极子臂的延长线上任一点的场强:
点电荷+q 和 -q 单独在A 点产生的场强的大小分别为
根据场强叠加原理,A 点总场强的大小为:
当 时 ,结果得
EA的方向与电矩 P 的方向一致
(2) 求电偶极子中垂线上的场强分布:
两电荷在B点产生的场强的大小
考虑到 ,故总场强大小为:
场强EB与电偶极子的电矩 P 反向
电偶极子在均匀电场中所受力矩:
[例] 求均匀带电圆环轴线上的场强分布,设 圆环半径为a,带电荷总量为Q 。
在轴上任取一点P ,其距圆心为 z 。
在圆环上A 处取电荷元
它在 P 点产生的场强的大小为:
dE 可分解为沿 z 轴的分量 和垂直于 z 轴的分量 , 由对称性分析可知,任意一条直径两端的两个同样大小的线电荷元 和 在P点所产生的场强在垂直于 z 轴方向上的分量 和 大小相等、方向相反、相互抵消
只有沿z轴方向上的分量是相互加强的
整个圆环在P点产生的总场强沿z轴方向
Prblem-slving strategy : Calculating Electric Field
1. Units : When perfrming calculatins that invlve the Culmb cnstant, K, charges must be in culmbs and distances in meters. If they appear in ther units, yu must cnvert them.
2. Applying Culmb’s law t pint charges : It is imprtant t use the superpsitin principle prperly when dealing with a cllectin f pint charges. When several pint charges are present, the resulting frce n any ne is the vectr sum f the individual frces due t the ther pint charges. Be very careful in the manipulatin f vectr quantities.
3. Calculating the electric field f pint charges : Remember that the superpsitin principle can be applied t electric fields, which are als vectr quantities. T find the ttal electric field at a given pint, first calculate the electric field at that pint due t each individual pint charge. The resultant field at the pint is the vectr sum f the fields due t the individual pint charges.
4. Cntinuus charge distributins : When cnfrnted with prblems that invlve a cntinuus distributin f charge, at sme pint yu must replace the vectr sums fr evaluating the ttal electric field by vectr integrals. The charge distributin is divided int infinitesimal pieces, and the vectr sum is carried ut by integrating ver the entire charge distributin.
5. Symmetry : Whenever dealing with either a distributin f pint charges r a cntinuus charge distributin, take advantage f any symmetry in the system t simplify yur calculatins.
电场线 — 形象描述电场在空间的分布情况。
(2) 通过垂直于场强E 的单位面积的电场线数在数值
(1) 电场线上每一点的切线方向表示该点场强的方向。
上等于该点处E的量值。
Small pieces f thread suspended in il align with the electric field.
The number f lines leaving the psitive charge equals the number terminating at the negative charge .
(2) 任何两条电场线不能相交。
(1) 起于正电荷 (或无穷远),止于负电荷 (或无穷远) 。
(3) 电场线越密的地方,场强越大; 电场线越疏的地方,场强越小。
Quick quiz 2
tw lines leave the charge +2q fr every ne that terminates n -q
电通量:电场强度对面积元 的通量称为电通量
对一个曲面的电通量,可以写成积分形式
面元法线的正方向规定为 从封闭曲面的内侧指向外侧
在有电场线穿出封闭曲面的地方
在有电场线穿入封闭曲面处
高斯定理: 1. 表述:通过任意封闭曲面的电通量 等于所有包围在该曲面内的电荷的代数和除以 ,而与闭合曲面外的电荷无关。
2. 证明:⑴ 以正电荷q为中心,以任意半径r作一球面S,通过此球面的电通量为⑵ 在上述球面内作一任意形状的封闭曲面 包围此电荷,则从q发出的电场线必全部通过 ,因而通过 的电通量也应等于 。
⑶ 封闭曲面不包围点电荷q ,从点电荷q 发出的电场线中,凡是穿进封闭曲面
⑷ 封闭曲面内包围多个点电荷时,第i个 点电荷对该曲面的电通量的贡献为
Quick quiz 3
[例] 半径为R 的导体球壳均匀带有正电荷 q , 求球壳内外空间中场强分布。
先考虑球外某点P 处的场强:
场强的分布也具有球对称性
以球心O 为中心,以r =OP为半径作一高斯球面S
球面上各点的场强大小相等,方向沿半径指向外面
同理,求带电球壳内的场强分布时,在球壳内以r 为半径作高斯球面,因球面内没有电荷,故得
根据高斯定理,通过球面S 的总电通量为:
而 , 因而可得
场强的大小与离开球心的距离r 有如下函数关系:
在 r =R 的球壳上,场强似乎发生了突变,但事实上,电荷的分布总占有一定的球壳厚度,可以证明,在无限靠近球面的外层到没有电荷的内层上,场强是逐渐衰减到零的。
[例] 原子核可近似等效为均匀带电球体,已知其半 径为R,带电总量为Q,求核内、外的电场分布。
电荷分布具有球对称性
球外任一点的场强用高斯定理可得
对球内任一点 P 求场强:
以OP 为半径作一高斯球面
所包围的电荷为 :
球内任一点的场强
球内场强随r 增大而线性增加,球外场强与 成反比
[例] 已知无限大均匀带电薄平板的面电荷密度 为 ,求空间的场强分布。
电荷分布具有平面对称性
离开平面等距离的各点场强大小
相等,场强方向与平面垂直。
通过两底面的电通量分别为ES
通过整个闭合圆柱面的电通量:
当 时,场强方向垂直指向两侧
当 时,场强方向从两侧垂直指向平面
上述结果表明,无限大均匀带电平板两侧的场强大小与位置无关,是均匀电场。实际上,不存在无限大平板,但当带电平板的尺度比考察点到平面的距离大得多,且考察点不靠近带电平板边缘时,可将带电平板看成无限大。
电荷分布具有轴对称性
[例] 求无限长均匀带电圆柱面内外的场强分布,已 知圆柱半径为R , 单位长度圆柱面带电量为 。
此圆柱的上、下底面的法线与E垂直
离开圆柱中心轴线为r 处的场强大小相 等,方向垂直于圆柱面,沿半径方向。
设P 为圆柱外一点,其到轴的距离为r , 作一同轴封闭圆柱面为高 斯面,使其侧面通过P 点,高为h。
高斯面所包围的电荷为 ,根据高斯定理
求P点在圆柱内的场: 由于圆柱内无电荷
通过此高斯面的电通量为
在点电荷q 产生的电场中,试探电荷 从a 点运动到b 点时电场力做的功为
沿闭合路径移动一周回到起点,则
静电场的环路定理 静电场是保守力场
1. 电场中a、b 两点的电势差为
电势能 类似于重力场,对静电场引进电势能的概念: 静电场力对 所做的功等于 的电势能的 减少量:
Quick quiz 4
2. 空间任一点的电势为
3. 电势零点的选取:若带电体系的电荷分布在有限大小的空间里,通常选择无穷远处为电势零点。若带电体系的电荷分布延伸到无限远,可在电场中选一个合适的位置作为电势的参考零点。例如对无限长带电圆柱面,可选柱面为电势零点。
Quick quiz 5
[例] 求点电荷q 所产生的电场中各点电势的分布。
[例] 求电偶极子在远处产生的电势。
由电势叠加原理, P 点的电势为
式中P 为电偶极矩, 为由O 指向P 的单位矢量
[例] 求半径为R ,均匀带电的球体产生的电 势的空间分布,已知球体带电总量为Q 。
[解] 由前已知均匀带电球体内外的场强分布为
以无限远处为电势零点,球体外任一点P 距离
球心的距离为r ,则P 点的电势为
再设球内任一点 到球心的距离为r ,则 点的电势为
以上结果表明,在r =R 处电势是连续分布的。
Prblem-slving strategy : Calculating Electric Ptential
1. When wrking prblems invlving electric ptential, remember that it is a scalar quantity, and s there are n cmpnents t cnsider. Therefre, when using the superpsitin principle t evaluate the electric ptential at a pint due t a system f pint charges, simply take the algebraic sum f the ptentials due t each charge. Yu must keep track f signs, hwever.
2. As with ptential energy in mechanics, nly changes in electric ptential are significant; hence, the pint where the ptential is set at zer is arbitrary. When dealing with pint charges r finite-sized charge distributin, we usually define V=0 t be at a pint infinitely far frm the charges. If the charge distributin itself extends t infinity, hwever, sme ther nearby pint must be selected as the reference pint.
3. The electric ptential at sme pint P due t a cntinuus distributin f charge can be evaluated by dividing the charge distributin int infinitesimal elements f charge dq lcated at a distance f r frm the pint P. This element is then treated as a pint charge, and s the ptential at P due t the element is
The ttal ptential at P is btained by integrating dV ver the entire charge distributin. Fr many prblems, it is pssible in perfrming the integratin t express dq and r in terms f a single variable. T simplify the integratin, it is imprtant t give careful cnsideratin t the gemetry invlved in the prblem.
4. Anther methd that can be used t btain the ptential due t a finite cntinuus charge distributin is t start with the definitin f the ptential difference given by
If E is knwn r can be btained easily (e.g. ,frm Gauss’s law), then the line integral f can be evaluated.
[Ex] Ptential due t a unifrmly charged ring
Find the electric ptential at a pint P lcated n the axis f a unifrmly charged ring f radius a and ttal charge Q .The plane f the ring is chsen perpendicular t the x axis.
Let us take P t be at a distance x frm the center f the ring.
[Reasning and slutin]
The charge element dq is at a distance equal t frm pint P . Hence, we can express U as
In this case, each element dq is at the same distance frm P . The term can therefre be remved frm the integral, and U reduces t
The nly variable in this expressin fr U is x.
[Quick Quiz 1]
Object A has a charge f +2C, and bject B has a charge f +6C. Which statement is true?
(a) FAB=-3 FBA (b) FAB= - FBA (c) 3FAB= - FBA
[Quick Quiz 2]
In fair weather, an electric field ccurs at the surface f the Earth, pinting dwn int the grund. What is the sign f the electric charge n the grund in fair weather?
[Quick Quiz 3]
Fr a gaussian surface thrugh which the net flux is zer, the fllwing fur statements culd be true. Which f the statements must be true?
N charges are inside the surface. The net charge inside the surface is zer. The electric field is zer everywhere n the surface.(d) The number f electric field lines entering the surface equals the number leaving the surface.
[Quick Quiz 4]
If an electrn is released frm rest in a unifrm electric field, des the electric ptential energy f the charge-field system increase, decrease, r remain the same?
相关课件
这是一份高中物理人教版 (新课标)选修32 库仑定律授课课件ppt,共25页。PPT课件主要包含了第一章《静电场》,第二节《库仑定律》,库仑定律,点电荷,思考题,ABD,库仑的实验,库仑扭秤1,库仑扭秤3,库仑扭秤2等内容,欢迎下载使用。
这是一份高中人教版 (新课标)2 库仑定律复习课件ppt,共21页。PPT课件主要包含了比较F与QF与r,测量变换法,改变B的电荷量等内容,欢迎下载使用。
这是一份人教版 (新课标)选修32 库仑定律评课课件ppt,共42页。PPT课件主要包含了电荷量,0×109,点电荷,两电荷连线,可忽略不计,矢量和,图1-2-1,图1-2-2,图1-2-3,图1-2-4等内容,欢迎下载使用。









