






人教版初中英语语法系列---动词课件
展开eat 吃eat up 吃光
have 吃三餐have breakfast / have lunch / have dinner
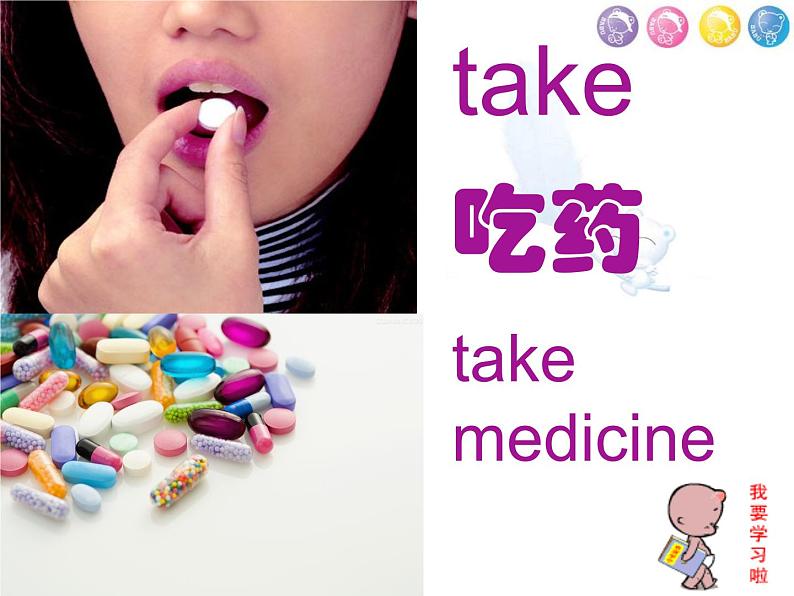
take 吃药take medicine
drink 喝drink tea/drink milk/drink cffee
play玩play game/play ftball
have拥有I have a watch.
Have 上(课),举行have art class上美术课have Chinese class上语文课have English class上英语课have math class上数学课have music class上音乐课have P.E. class上体育课have science class上科学课have a lk看一看have a picnic举行野餐
speak 说(某种语言),讲话I can speak Chinese and English. 我会说汉语和英语。Dn’t speak ludly in library.不要在图书馆大声讲话。
talk 交谈A BA talk with BA与B 交谈
say 说+(说的内容)I can nt say a wrd just nw.
read读,看 read a magazine 阅读杂志read bks 看书
walk 走路,散步
d hmewrk做作业
d husewrk做家务
d mrning exercises晨练
d the dishes洗碗碟
clean 打扫,清洁
谓语动词
谓语动词就是能在句子中作谓语的动词(独立做谓语,或者构成复合谓语皆可)
谓语动词就是不能在句子中作谓语的动词
四.动词的分类(谓语动词)
实义动词考点:单三,现在分词,过去式,过去分词
+宾语+双宾语+复合宾语:自身意思完整, 无需接宾语。
另外,实义动词按动作是否持续,可划分延续性动词和非延续性动词(短暂性动词)。
动词+宾语I like this bk very much.主语: I (谓语动词的发出者)谓语: like (谓语动词)宾语:this bk (谓语动词的对象)又如: I have a dream.
2) 动词+双宾语(即:动词+间接宾语+直接宾语,其中,间接宾语是人,直接宾语是物。 )Lucy passes me the salt.主语: Lucy (谓语动词的发出者)谓语: passes (谓语动词)间接宾语: me (谓语动词的对象的归属)直接宾语: the salt (谓语动词的对象)
3) 动词+复合宾语(即:动词+宾语+宾语补足语,宾补为了补充说明宾语的身份、特征、状态或所做的动作。)We call him Jack . I saw the children play in the park yesterday.主语: I (谓语动词的发出者)谓语: saw (谓语动词)宾语: the children (谓语动词的对象)宾补: play in the park (省略了t的不定式,补充说明宾语的状态)
后跟不定式做宾语补足语时,需要把不定式中的t 省去 的动词:1感:feel 2听,hear ,listen t 3 使,let ,make ,have 4看,see, lk at ,watch, ntice ,bserve (其实是5看)半帮助 help help sb (t) d sth. 其中的t 可有可无。
后跟不定式做宾语补足语时,需要把不定式中的t 省去 的动词:1感:feel 2听:hear ,listen t 3 使:let ,make ,have 4看:see, lk at ,watch, ntice ,bserve半帮助 help sb. (t) d sth. 其中的t 可有可无。
当然,在这些词的后面可以作宾补的,不仅仅是省略t的动词不定式,还可以是现在分词和过去分词。----非谓语动词细讲
1. My mther made me _____dwn the radi just nw. A. turned B. turn C. was turning D. t turn2. Nancy is really a hard-wrking student. We ften see her _____ bks in the classrm. A. read B. t read C. reads D. reading
自身意思完整,无需接宾语。Hrses run fast. 主语: Hrses (谓语动词的发出者)谓语: run (谓语动词)
(1).有些动词既可以作及物动词,也可以作不及物动词。及物动词study --We study English. 主语 谓语 宾语不及物动词study --We study hard. 主语 谓语 副词作状语
(2).有些不及物动词要与别的词搭配在一起,构成短语动词,相当于一个及物动词。不及物动词+介词 (动介短语)Listen t the teacher carefully.注意: 介词后只能接 作宾语。宾语的位置在介词后。
不及物动词+副词 (动副短语)He picked it up and gave it t me .He picked up the key and gave it t me .注意: (1). 动副短语后 代词(常it, them)作宾语时,代词要放在动词与副词之间。(2). 动副短语后名词作宾语时,名词词要放在动词与副词之间,或者副词之后皆可。
不及物动词+副词+介词 (动副介短语)Let’s g n with ur wrk ! 继续进行,继续做某事He gets alng well with his classmates.与…相处(怎么样)…He gt dwn t his wrk after the hlidays. 开始认真对待注意: 这类短语动词的宾语位置,与动介短一样,只能在介词后。
不及物动词+名词+介词 (动名介短语)Please pay attentin t the phrasesin the article. 请注意文章中的短语。We can make gd use f air. 我们可以充分利用空气。注意: 这类短语动词的宾语位置,与动介短一样,只能放在介词后。
be+形容词+介词 We are gd at swimming. 擅长(做)某事I am interested in this famus wrk.对…感兴趣She is satisfied with what I did.对…感到满意
be+形容词+介词 be able t 能够 be wrried abut 对……感到担心be interested in 对……感兴趣 be weak in 在方面不行 be gd at 擅长…… be excited at 对……感到兴奋 be surprised at 对惊讶 be angry at 对感到生气Be busy with 忙于做 be familiar with 对 熟悉be satisfied with 对---感到满意
感兴趣在某方面不行用in,擅长与生气惊讶兴奋用at,忙于做对熟悉用 with
be friendly t 对……很友好 be superir t 胜过be inferir t 不及be (quite) equal t 相当,差不多be fnd f 喜欢 be afraid f 害怕be tired f 对……感到厌烦 be wrthy f 值得 be prud f 对自豪be absent frm 缺席be famus fr 因而著名be ready fr 为准备好
友好胜过不及差不多用t,喜欢害怕厌烦值得自豪用f,因..而著名为..准备好用fr
延续性动词: 动作是可以持续的,可以和表示一段时间的状语连用。非延续性动词:动作是瞬间完成的,一经发生立即结束。不能和一段时间的状语连用。
助动词本身无意义或者意义不全。不能独立作谓语。跟主要动词构成谓语,表示疑问,否定及各种时态。
d / dn’t des / desn’tdid / didn’t
have /haven’t has / hasn’thad / hadn’t
am / am ntIs / isn’tare/ aren’t
shall / shuld
will / wuld
1. Be动词在时态中的运用:be+动词现在分词(1). 在现在进行时中:Eg. We are talking nw.(2).在过去进行时中:Eg. We were talking at this time yesterday.
助动词be的2个用法
2. Be动词在被动语态中的运用:be+动词的过去分词Eg. Yu are wanted n the phne, Tm !Eg. My favrite ring is lst.
1. 助动词have在时态中的运用:have(has,had)+动词过去分词构成完成时。(1). 在现在完成时中:We have studied English fr five years. He has gne t Shanghai Since last year.(2).在过去完成时中:The bus had already left by the time Igt there.
助动词have的用法
1. 助动词d,des,did在疑问句中的运用: D(des,did)+主语+实义动词原形+宾语+…----D yu live in China ?2. 助动词d,des,did在否定句中的运用:主语+dn’t(desn’t,didn’t)+实义动词原形+宾语+…He didn’t play basketball yesterday.
助动词d的6个用法
3. 助动词d,des,did在代替前面出现的动词,以免重复:----D yu live in China ?----Yes, I d.(代替live in China)4. 助动词d,des,did在动词原形前,加强语气:I d return the bk t the library. 我的确把书还回图书馆了。
5. 助动词d,des,did在反意疑问句中的运用:(1)前肯定,后否定的反意疑问句: 主语+实义动词+宾语+…, dn’t/ desn’t/ didn’t + 主语 ?----He wrks in a schl, desn’t he?----Yes, he des.(肯定问话人的回答) / N, he desn’t.(否定问话人的回答)(2)前否定,后肯定的反意疑问句: 主语+助动词dn’t/ desn’t/ didn’t+实义动词原形+宾语+…, d/ des/ did + 主语 ?----He desn’t wrk in a schl, des he?----Yes, he des. (否定问话人的回答) / N, he desn’t. (肯定问话人的回答)
1. He hardly speaks English, _____ he? A. des B. desn’t C. is D. isn’tThis is a beautiful picture, _____ ? A. isn’t this B. is this C. isn’t it D. is it
反意疑问句中:陈述部分主语是this,that 时,反义疑问部分主语应用 it 。陈述部分主语是these,thse时,反义疑问部分主语应用 they。
6. 助动词d,des,did在倒装句中的运用:(1). 肯定句的倒装: 第一主语+实义动词+宾语+…, s +d/ des/ did + 第二主语.They helped the farmers , s did we.(2). 否定句的倒装:第一主语+dn’t /desn’t /didn’t+实义动词原形+宾语+…, Neither/ Nr +d/ des/ did + 第二主语.They didn’t help the farmers , neither did we.They didn’t help the farmers , nr did we.
对句子进行否定和疑问D yu get up early every day?I didn’t (没)have lunch yesterday.Will yu be back sn?He hasn’t (没)finished the wrk yet.在反意疑问句中He wrks in a schl, desn’t he?She has never been there, has she?在倒装句中They helped the farmers , s did we.I wn’t visit the famus singer,neither will he.
连系动词 (系动词)
连系动词本身有词义。不能独立作谓语。没有被动语态。不用于进行时态。跟表语构成复合谓语。说明主语的状态,性质,特征或身份。
连系动词 (系动词)
常见的系动词是变化连系动词 get,turn,becme,make感官连系动词 lk,sund,smell,taste,feel表象连系动词 seem, appear, lk持续连系动词 stay, keep, stand, lie, rest状态连系动词 be The day gets lnger and lnger. He lked happy. I feel hungry.
感官连系动词,有时相当于被动语态主语:被感觉的对象谓语:感官连系动词表语:被感觉对象的状态,性质,特征The flwers smell very sweet.
与名词、数词、形容词、介词连用I am a dctr. He is ten.They are tired.The cat is under the table.
There be 句型用于不可数名词和可数名词单数之前There is a pen n the desk.There is sme water in the glass.用于复数名词之前There are sme sheep in the hill.用于一般将来时There is ging t be a film in ur schl next Sunday.用于一般过去时There was a bk n the desk yesterday. There used t be (过去常)a tall tree here.
情态动词后面跟动词原型无论否定、疑问、倒装句、或反意疑问句都可以用情态动词只有时态变化,没有人称变化
情态动词
1. 常见的情态动词: can / culd (3点)在表示请求允许,意为“可以,能”两者可以互换, culd比can语气更委婉。----Can I help yu?----Culd yu pen the windw?肯定答语: Yes, …. can.否定答语: N, ….can’t.
1. 常见的情态动词: can / culd (3点)在表示能力,意为“能够,会”仅仅在表示能力时, culd是can的过去式。I can swim. / I can’t swim.I culd swim at the age f five.C. 在表示推测,意为“可能”,一般用于否定句或疑问句。That can’t be Mary. She’s in hspital.
2)May/ Might (2点)(might不是may的过去式)表示请求允许,意为“可以,能”May 用在第一人称的一般疑问句时,May I use yur bike?肯定形式: Yes, … can. 否定形式: N, … can’t. / N, … mustn’t.B. 表示表示推测,意为“或许,可能”,最不确定的推测。He might cme tmrrw, but I am nt quite sure.他明天可能来,但我不是很确定。
3)Must (4点) A.表示主观看法,意为“必须,应该”I must g nw.Yu mustn’t play in the street.B. 表示推测,意为“一定,肯定”,最肯定的推测,仅仅用于肯定句(must表示推测时,不能用于否定句)。----There’s smene kncking n the dr.----It must be Jim.
3)Must (4点)C. must的否定式mustn’t有“禁止”的意思。The children mustn’t play with fire. 孩子不能玩火。 D.以must开头的一般疑问句,肯定回答:Yes, …must.否定回答:N,…needn’t或dn’t have t.----Must I g hme nw ?----N, yu needn’t. / N, yu dn’t have t.
4)need (1点)表示需要,必要,意为“必须” ,主要用于否定句和疑问句中。Must I g hme nw ?肯定回答: ---- Yes, yu must.否定回答: ----N, yu needn’t. / N, yu dn’t have t. (不必须,不必要)
Need既是实义动词,也是情态动词。详见下页。
实义动词 Need:1. need t d sth. 需要做某事 I need t d my hmewrk. 我需要做我的作业。2. need ding sth. 需要(被)做某事 The flwer needs watering. 花需要(被)浇水。提问时用d系的助动词提问, 用d系的助动词回答。Des he need t wash his hands? 他要不要洗手?Yes, he des. / N, he desn’t.情态动词 Need: 1. need d sth. 必须做某事Need开头的一般疑问句。肯定回答用must,否定回答needn’t.Need I finish my hmewrk? 我必须完成家庭作业吗?Yes, yu must. / N,yu needn’t.
Must开头,回答大致相同
5)Must /have tMust 表示主观意愿的“必须”,它是常规的情态词,因此没有时态和人称变化。否定句用Mustn’t,否定回答用needn’t /dn’t have t.I must g nw.Yu mustn’t play in the street.----Must I clean the rm nw?----N, yu needn’t. / yu dn’t have t.have t表示客观条件的限制的“不得不”,它并非常规的情态动词,因此它有时态和人称变化。需要助动词来否定和疑问。He had t wash his clthes. (一般过去时)I dn’t have t carry the big bx. (助动词来否定)
6)will / wuld (2点) A. 表示意愿,自愿做或者主动提出做某事。She asked if I wuld g with them.她问为是否愿意跟他们一起走。B. 表示征求意见或者提出请求,用于第二人称的疑问句中。Will yu please pst the letter fr me ?请帮我寄了这封信好吗?
7)shall (4点) A. (用于第一人称) 表示将来会,“将,会” I shall be thirty next year. 明年我就三十岁了。 B.(用于第一,三人称疑问句中) 表示说话人征求对方的意见或请求, “好吗”Shall we begin nw? 我们现在开始好吗? Shall I turn n the lights? 我开灯好吗? C. (用于第二、三人称陈述句中) 表示说话人的意图、允诺、警告、命令、决心等, “必须,应,可” He shall stay in bed. 他必须躺在床上。 He says he wn't g, but I say he shall. 他说他不去,但我说他必须去。
7)shall (4点)D. (用于第三人称中) 在条约,规定,法令等文件中表示义务或者规定, “应该,必须” N reader shall remve a bk frm the librarywithut permissin.未经允许,任何读者不准把书带出图书馆。注意:shuld 不是 shall的过去式。
8)shuld (3点)表示劝告、建议、命令。 “应该,必须” Yu shuld g t class right away. 你应该马上到教室去。B. (用于第一,三人称疑问句中) 表示说话人征求对方的意见或请求, “好吗”Shuld I pen the windw? 我把窗户打开好吗?C. 表示推测。 “应该,可能” It shuld be Jack wh was late this mrning.今天早晨应该是杰克迟到了。
7)shall (4点)D. (用于第三人称中) 在条约,规定,法令等文件中表示义务或者规定, “应该,必须” N reader shall remve a bk frm the librarywithut permissin.未经允许,任何读者不准把书带出图书馆。
Can /May/Must / Need 引导一般疑问句(第一人称) 的答语Can I Yes, yu can. N, yu can’t. May I Yes, yu can. N, yu can’t. / N, yu mustn’t.Must I Yes, yu must. N, yu needn't. / N, yu dn't have t. 3. Need I Yes, yu must. N, yu needn't.
1. Yu _____ play with the knife, r yu _____ hurt yurself. A. may nt ; may B. can’t ; need C. needn’t ; must D. mustn’t ; may2. It desn’t lk like rain, s yu _____ bring yur umbrella with yu. A. shuldn’t B. mustn’t C. can’t D. needn’t
---- Lk! The man at the gate _____be ur head master. He is always standing there every mrning. ---- N, it _____ be him. He is hlding a meeting in the ffice nw. A. must; can’t B. must; mustn’t C. can’t; can’t D. can’t; mustn’t4. ---- _____I brrw yur MP4? ----Sure. Here yu are.May B. MustC. Shuld D. Need
5. ---- May I watch TV fr a while? ---- N, yu _____. Yu have t finish yur hmewrk first. A. shuldn’t B. needn’t C. mustn’t D. wn’t4. Children under 16____ nt drive a car in the street.shuld B. culd C. wuld D. will
表示法律条文规定的权利义务时,常用shuld
实义动词指的是有具体行为意思的动词。实义动词在句中可以做谓语动词和非谓语动词。做谓语动词的用法 动词会有四种形式:单三,现在分词,过去式,过去分词
4. 做非谓语动词的用法(指出现在谓语动词之后的动词,它受前面谓语动词的限制) 做非谓语的动词会有三种形式:(1)不定式 (t d) / 省略t的不定式(d) (2) 现在分词 & 动名词 : ding(3)过去分词形式
掌握作谓语动词时:四种形式的变化规律He wrks in the ffice. (单三)We are dancing tgether.(现分)I caught a cld last week. (过去式)She has watered the flwer. (过分)
引出:动词时态(初中:八种)
概念: 表示习惯、经常性的动作结构: d、 des标志语: usually、ften、never、 smetimes、nce a week、 twice a mnth、every year 等
1.经常性,习惯性的动作。When d yu usually have breakfast ?2. 表示主语所具有的特征,性格,能力或状态等。She is a middle schl student.3. 客观事实,普遍真理。 The earth ges arund the Sun.4. 主将从现原则 (在时间状语从句和条件状语从句中)。If it rains tmrrw, we wn’t g t the park.
5. 表正在进行的动作。There ges the bell.6. 表示安排或计划好的将要发生的动作。如:火车,飞机的时刻表。The train starts at 7:30 a.m.
动词的单三形式的构成(在一般现在时中):
The twins ___________(wash) the clthes every day.Smetimes he ________ (play) basketball ver there.Hw ften ____ Sally ______(sing)?
一般现在时中标志词:Usually,ften,never,smetimes,nce a week、 twice a mnth,every day ,every year 等
概念: 表示现在正在发生的动作结构: be (is, am, are) + ding标志语: Lk! 、 Listen! 、can yu see 或者 nw 、 these days
动词-ing形式的构成(在进行时态中):
writingtaking
gettingrunningswimming
1. 表示此时此刻或现阶段正在进行的动作。They’re having a meeting. 他们在开会。(此时此刻)I’m studying at an evening schl. 我在上夜校。(现阶段)2. 表示计划或安排好了的将来动作(常见: g,leave, arrive , start, fly),常与一个表示将来的时间状语连用。Mike is cming hme n Thursday. 迈克星期四回来。They’re having a party next week. 下星期他们将开一个晚会。
注:表示安排将要做的事,人作主语宜用现在进行时,事物作主语,宜用一般现在时。I’m nt ging ut this evening. 今晚我不准备出去。(不宜说I dn’t…) The cncert starts at 7: 30. 音乐会七点半开始。
3. 现在进行时与always, ften, frever等连用表示赞扬、厌烦等语气。如:Yu’re always interrupting me! 你老打断我的话!(抱怨) My father is always lsing his car keys. 我爸老丢车钥匙。(不满) She’s always helping peple. 她老是帮助别人。(赞扬)
稍后,我们将学习: 有些静态动词通常不用于进行时态。
现在进行时的肯定句(1)第一人称单数:主语 + am + 现在分词 + ……eg. I am watching TV. 我现在看电视。(2)第三人称单数:主语 + is + 现在分词 + ……eg. She is washing the dishes. 她正在洗澡。(3)第二人称及复数人称:主语 + are + 现在分词 + ……eg. They are playing games. 他们正在做游戏。现在进行时的否定句 主语 + 相应be动词 + nt + 现在分词 + …… eg. He isn't watching TV. 他没在看电视。 I am nt cking. 我没有在做饭。 We aren't haveing English calss. 我们没在上英语课。
现在进行时的一般疑问句 相应be动词 + 主语 + 现在分词 + ……?eg. Are yu dancing? 他们正在跳舞吗?Is he drawing a picture? 他正在画一张画吗?Are yu talking with yur friend? 你正和你的朋友谈话吗?现在进行一般疑问句的答语(1)肯定回答: Yes, 主语 + 相应be动词。(2)否定回答: N, 主语 + 相应be动词 + nt 。eg. Are yu listening t the music?你正在听音乐吗? Yes, I am. / N, I am nt. 是的,我正在听。/ 不,我没在听。 Is Aunt Wang knitting a sweater? 王阿姨正织毛衣吗? Yes, she is. / N, she isn't. 不,她没有。
现在进行时的特殊疑问句特殊疑问词 + 相应be动词 + 主语 + 现在分词 + ……?其实就是特殊疑问词+一般疑问句eg. What are yu ding? 你正在干什么? Wh is singing a sng? 谁在唱歌呢?Why are they cleaning their rm? 他们为什么在打扫房间?现在进行时特殊疑问句的答语回答特殊疑问时,根据不同的疑问词的情况来决定回答方式。回答what提问时,答语是现在进行时的肯定形式;回答wh提问时,只需说明主语是谁,再加相应的be动词即可。eg. --What is he ding? --He is writing a letter. 他正在干什么?他正在写信。--Wh is swimming in the lake? --Jim is. 谁正在湖里游泳?吉姆正在游泳。
不能用进行时的静态动词 事实状态的动词 have, belng t(属于), cst, wn, exist, include, matter, weigh, cntinue 例如: I have tw brthers. This huse belngs t my sister.2) 心理状态的动词 knw, realize, think/see(理解,领会), believe, suppse, imagine, agree, remember, want, need, frget, prefer, mean, understand, lve, hate 例如: I need yur help. He lves her very much.
3 ) 非延续性动词(短暂性动词) accept(接受), refuse(拒绝), give(给予) receive(收到), cmplete/ finish(完成), allw, decide. 例如: I accept yur advice. 4) 系动词 seem, remain, lie, see, hear, smell, feel, taste, get, becme, turn 例如: Yu seem a little tired.
The twins ___________(wash) the clthes nw.Lk! He ________ (play) basketball ver there.Listen! ______ Sally _______(sing)?
are washing
概念: 表示过去发生的动作结构: did标志语:yesterday , the day befre yesterday , last + 时间 (week, mnth, year) , this mrning,时间 + ag , just nw , a mment ag , in + 过去的时间
1)在确定的过去时间里所发生的动作或存在的状态常用的时间状语有:yesterday, last week, an hur ag, the ther day, in 1982等。 例如: Where did yu g just nw?2)表示在过去一段时间内,经常性或习惯性的动作。 例如: When I was a child, I ften played ftball in the street.Whenever the Brwns went during their visit, they were given a warm welcme.
carriedcried
stppedplanned
动词-ed形式的构成(在一般过去时中):
不规则动词原型--过去式
set --set (放)sing--sang (唱歌)sit--sat (坐)sleep--slept (睡觉) speak--spke (说话) spend --spent(花费)stand --std (站立)swim --swam (游泳)teach--taught (教)tell --tld (告诉)think--thught (认为)thrw--threw (投掷)understand--understd (懂得) wear--wre (穿) will--wuld (将要) win--wn (获胜)
am (is)-was (是) are-were(是)g-went(走)cme-came(来)take-tk(拿) have (has)-had(有)begin--began (开始) bring--brught (拿来)can--culd (能)catch--caught (捉住)cut--cut (砍,割)d/des--did (做,干)draw--drew(画画,拉) drink--drank (喝)drive--drve (驾驶)eat--ate(吃)fall--fell (跌倒,落下)feel--felt (感觉)fly--flew (飞)
get--gt (获得)give--gave (给)grw--grew (生长)keep--kept(保持)knw--knew(知道,认识)learn--learnt(学习)leave--left (离开)let--let(让)lie--lay(躺,平放)make--made (使得,做)may--might (可以)must--must (必须)read--read (读)ride--rde (骑)ring--rang (鸣铃) run--ran (跑)say --said (说)see --saw (看见)sell --sld (卖)send--sent (送)
1.Be动词的一般过去时 在没有实义动词的句子中使用be动词, am is 的过去式为was; are的过去式为were 肯定句式:主语 + be (was , were) + 其它. 否定句式:主语 + be (was , were) + nt + 其它. 一般疑问句:Be (was , were) + 主语 + 其它?特殊疑问句: 特殊疑问词+Be (was , were) +主语+其他? What was yur frmer name? 你以前叫什么名字? 注:在这种构成中,be动词有人称和数的变化,即要根据主语选用was / were。Be动词分为单数和复数,was是表示单数,were是表示复数。
2. 实义动词的一般过去时 肯定句式:主语 + 动词(过去式)+ 其它. 否定句式:主语 + didn’t + 动词(原形)+ 其它. 【did nt = didn’t】 一般疑问句:Did + 主语+ 动词(原形)+ 其它?【d , des的过去时均为did】 特殊疑问句: 特殊疑问词+d/des过去式+主语+动词原形+其他?Why did he late fr schl last Mnday? 上星期一他为什么迟到?注:did和didn’t 是构成一般过去时的助动词,其特点是要在其后跟动词的原形。
3. 情态动词的一般过去时 含有情态动词的一般过去时与含有Be动词的一般过去时,是十分相似,请注意观察。 肯定句式:主语 + 情态动词的过去式 + 其它. 否定句式:主语 + 情态动词的过去式 + nt + 其它. 一般疑问句: 情态动词的过去式 + 主语 + 其它?特殊疑问句: 特殊疑问词+情态动词的过去式+主语+动词原形+其他? What culd she d twenty years ag? 20年前她能做什么? 注:情态动词的过去式:can→culd , may→might , must→must ,will-wuld,shuld-shuld。
The twins ___________(wash) the clthes yesterday.The day befre yesterday he ________ (play) basketball ver there._____ Sally ______(sing) tw hurs ag?
3. Frank read an interesting bk abut histry. (改为一般疑问句) _______ Frank _______ an interesting bk abut histry?4. He cleaned his rm just nw. (划线提问)What________ he _______? 5. Thmas spent RMB 10 n this bk. (改为否定句) Thmas _______ _______ RMB 10 n this bk.
didn’t spend
概念: 表示已经发生的动作结构:助动词have (has) + 动词的过去分词( has 用于第三人称单数,have 用于其他所有人称。 )标志语:already、 yet、ever、 never、since…、fr…、
(1)现在完成时表示过去已完成动作,但对现在造成了影响或结果通常与表示包括现在在内的时间副词 just,already, befre, yet, never, ever等状语连用。例如: ① I have never(从未) heard f that befre.② Have yu ever(曾) ridden a hrse?
③ She has already(已) finished the wrk.④ Have yu milked the cw yet(还)? Yes, I have dne that already.⑤ I’ve just(刚) lst my science bk. 有时没有时间状语,多是一般疑问句。
(2)现在完成时表示过去已经开始,持续到现在,也许还会持续下去的动作或状态。可以和表示从过去某一时刻延续到现在(包括现在在内)的一段时间的状语连用。如:fr+时间段和since+时间点,以及 s far, nw, tday, this week (mnth, year) 等。例如:I haven’t seen her these days(这些天).She has learnt English fr 3 years(三年).
They have lived here since 1990(自1990).What has happened t the USA in the last 350 years(在过去的350年)?注意:表示短暂时间动作的词,如cme, g, die, marry, buy等的完成时不能与fr+时间段和since+时间点等表示一段时间的短语连用。
比较:Mrs. Darby lived in Kentucky fr seven years. (含义:达比太太已不再住在肯塔基州。)Mrs. Darby has lived in Kentucky fr seven years. ( 含义:现在还住在肯塔基州,有可能指刚离去) 注意: 用过去时表示现在,表示委婉语气。 1)动词want, hpe, wnder, think, intend 等。 Did yu want anything else? I wndered if yu culd help me. 2)情态动词 culd, wuld. Culd yu lend me yur bike?
have been (t)和have gne (t)的区别: ★ have / has been (t) 表示“曾经去过”某地,说话时此人很可能不在那里,已经回来。侧重指经历。★ have / has gne (t) 表示某人“已经去了”某地,说话时此人在那里,或可能在路上,反正不在这里。 试比较: He has been t Beijing. 他曾去过北京。 (人已回来,可能在这儿) He has gne t Beijing. 他已经去了北京。 (人已走,不在这儿)。
1)过去时表示过去某时发生的动作或单纯叙述过去的事情,强调动作;现在完成时为过去发生的,强调过去的事情对现在的影响,强调的是影响。2)过去时常与具体的时间状语连用,而现在完成时通常与模糊的时间状语连用,或无时间状语。
一般过去时与现在完成时之比较
◎ 一般过去时的时间状语有:yesterday, last week,…ag, in1980, in Octber, just nw, 具体的时间状语。◎ 共同的时间状语有:this mrning, tnight, this April/…, nw, nce, befre, already, recently,lately 等。 ◎ 现在完成时的时间状语有:fr, since, s far, ever, never, just, yet, till / until, up t nw, in past years, always, 等不确定的时间状语。
请大家认真分析比较下列三组例句:一般过去时: I saw this film yesterday. (强调看的动作发生过了。)现在完成时: I have seen this film. (强调对现在的影响,电影的内容已经知道了) 一般过去时: She returned yesterday. (她是昨天回来了, 强调动作已经完成)现在完成时: She has returned frm Paris. (她已从巴黎回来了,强调回来的意义)
一般过去时: He jined the League three years ag. ( 三年前入团,jined为短暂行为。)现在完成时: He has been in the League fr three years. (在团内的状态可延续)注意:句子中如有过去时的时间副词(如 yesterday, last week, in 1960/…)时,不能使用现在完成时,要用过去时。例如:(错)Tm has written a letter t his parents last night.(对)Tm wrte a letter t his parents last night.
1) 用于完成时的区别:延续性动词 表示经验、经历; I‘ve knwn him since then.我从那时起就认识他了。(表经历) 非延续性动词 表示行为的结果,不能与表示段的时间状语连用。 ( 但是,现在完成时的否定式,已成为一种可以延续的状态,因此可以和表示一段时间的状语连用。)He has cmpleted the wrk. 他已完成了那项工作。 (表结果)现在完成时的否定式:I haven’t heard frm him fr tw weeks.He hasn’t left here since 1990.
延续性动词与非延续性动词 的区别
2) 用于till / until 从句的差异:延续性动词用于肯定句,表示“做……直到……” ;非延续性动词用于否定句,表示“到……,才……”。 He didn't cme back until ten 'clck. 他到10 点才回来。He slept until ten 'clck. 他一直睡到10点。
3)用于 when / while 从句的差异: 在while(表示‘一段时间’)引导的从句中,不能用非延续性动词 (短暂性动词),但when可以,因为when可表示时间点,也可表示时间段。误:While I gt t the village, it was dark.正:When I gt t the village, it was dark.4)非延续性动词(短暂性动词)的肯定式的完成时不能和hw lng连用。误:Hw lng have yu brrw the bk?正:Hw lng have yu kept the bk?
将非延续性动词(短暂性动词)改为相应的延续性动词或短语和一段时间连用,其常用的方法有:a. 用相应的延续性动词替换的主要有:buy have brrw keep cme/g/becme be catch/get a cld have a cld get t knw knw be+名词 jin the Party be a Party member
延续性动词与非延续性动词 的转换
g t schl be a studentc. be+形容词/副词 leave be away (frm) die be dead put n be n finish/end be ver begin/start be n cme be here/in fall asleep be asleep g ut be utd. be+介词短语 g t schl be in/at schl jin the Army be in the Army
e.去掉短语中的短暂性动词cme t wrk wrk begin t study studyf. 把误句中表示一段时间的状语改为表示过去时间的状语,原动词的完成时改为过去时He cme here three mnths ag.
用 “It is/ has been +一段时间 +since(一般过去时)”结构。It is/ has been three mnths since he came here.用“多长时间+has passed + since(一般过去时)”结构: Three mnths has passed since he came here.
1. Yu dn't need t describe her. I ___ her several times. A. had met B. have met C. met D. meet
首先本题后句强调对现在的影响,我知道她的模样,你不用描述。再次,several times告知为反复发生的动作,因此用现在完成时。
2. --- I'm srry t keep yu waiting. --- Oh, nt at all. I ___ here nly a few minutes. A. have been B. had been C. was D. will be
等待的动作由过去开始,持续到现在,应用现在完成时。
3. I _____ my best friend since we were fur years ld. A. knw B. knew C. knwn D. have knwn
since引导的从句用一般过去时,主句用现在完成时。另外,还有句型:It is/ has been +一段时间 +since(一般过去时)
4. --- Have yu ever been anywhere fr a trip ?. --- A trip ? I ____ away frm my hmetwn even nce. A. went B. have gne C. have never been D. have been
现在完成时的标志词:s far, already , yet , ever , never , since… , fr…
The twins ___________(wash) the clthes fr an hur.He ________ (play) basketball since three years ag.Hw lng _____ Sally ______(sing) yet?
have washed
1、 概念:表示过去的过去。 2 、结构:had + 过去分词
-----------|----------------|--------------------|----> 那时以前 那时 现在
by the end f( 到…末为止): 跟过时用过完,跟现时用现完,跟将时用将完。at the end f (在末):后边可以跟时间和地点名词,用于各种时态
1)过去完成时表示:过去某一时刻或者某一动作之前完成的动作或状态。句中常用by, befre, until, when等词引导的时间状语。By the end f last year we had built five new huses.I had learnt 5000 wrds befre I entered the university.2)过去完成时还可以表示:过去某一时刻之前发生的动作或者状态持续到过去某个时间或者持续下去。Befre he slept, he had wrked(已工作) fr 12 hurs.
3)在tld, said, knew, heard, thught等动词后的宾语从句。She said (that) she had never(从未) been t Paris.4)在过去不同时间发生的两个动作中,发生在先,用过去完成时;发生在后,用一般过去时。When the plice arrived, the thieves had run away(逃跑).
5)表示意向的动词,如hpe, wish, expect, think, intend, mean, suppse等,用过去完成时表示"原本…,未能…"We had hped that yu wuld cme, but yu didn't.6)过去完成时常用的时间状语: befre, by, until , when, after, nce, as sn as。He said that he had learned(学) sme English befre.By the time he was twelve, Edisn had began t(开始) make a living by himself.
1. When I gt the hspital, the patient____. A. has died B. died C. had died D. has dead
1. die 【死】 -----动词原形2. died 【死】 -----动词过去式,过去分词-----就是死这个动作成为了过去 dying 【死】 -----动词现在分词:he‘s dying.(他正在死去) -----也有形容词说【死亡的】 【垂死的】4. dead-----形容词----- 【死了的】 (一种状态), 【没有生气的】 , 【已结束的】5. the dead-----名词----- 【死者】6. death -----名词----- 【死亡】
2. Maria said that she________ never ________China befre . A. had; been t B. had; been C. has; been D. has; been t 3. He______ 2,000 wrds since last year. A. has learn B. has learned C. learns D. learned
4. Many bridges ______ by the end f last year . A. had been repaired B. has learned C. learns D. learned 5. Many wunded peple________ befre they ________ t the hspital.A. had been treated; sent B. were treated ; sent had been treated; were senttreated; sent
by the end f( 到…末为止): 跟过时用过完,跟现时用现完,跟将时用将完。at the end f (在末):后边可以跟时间和地点名词, 用于各种时态。
用一般过去时代替完成时 1) 两个动作如按顺序发生,又不强调先后,或用then,and,but 等连词时,多用一般过去时。When she saw the muse,she screamed. My aunt gave me a hat and I lst it.2) 两个动作相继发生,可用一般过去时;如第一个动作需要若干时间完成,用过去完成时。When I heard the news, I was very excited.3) 叙述历史事实,可不用过去完成时,而只用一般过去时。Our teacher tld us that Clumbus discvered America in 1492.
1. The ld man _____ tw days after he had been sent t hspital. A. died B. wuld die C. had died D. has died 2. Old McDnald gave up smking fr a while, but sn ______ t his ld ways. A. returned B. returns C. was returning D. had returned 3. I _____ t take a gd hliday this year, but I wasn’t able t get away. A. hpe B. have hped C. had hped D. hped 4. Helen _____ her key in the ffice s she had t wait until her husband _____ hme. A. has left; cmes B. left; had cme C. had left; came D. had left; wuld cme
1、 概念:表示从过去的某一时间看将要发生的动作或存在的状态 。 2 、结构: wuld/shuld+动词原形
它是一个相对的时态,即立足于过去某时,从过去的某一时间看即将发生的事情就要用这一时态。
二、基本形式: wuld/shuld+动词原形(其中 wuld 用于各种人称, shuld 只用第一人称)。They were sure they wuld win the final victry. 他们坚信会赢得最后胜利。 He didn’t expect that we shuld(wuld)all be there. 他没想到我们都在那里。 上述两个例句中的宾语从句谓语 wuld win 和 shuld(wuld)be 分别与其主句谓语 were sure 和 didn't expect 相对应。
三、过去将来时的一些其它表达形式: 1.was/were+ging t+动词原形 He said he was ging t try. 他说他准备试试。 2.was/were+t+动词原形 They said the railway was t be pened t traffic n May Day. 他们说这条铁路将在五一节通车。 3.was/were abut+动词原形,表示即将要发生的动作。 We were abut t g ut when it began t rain.我们正要出去天(突然)下起雨来。 4.过去进行时(一般多为动作概念较强的动词,如 g,cme, leave,start, pen,begin , arrive 等)也可用于表示过去将来。 I didn't knw when they were cming again. 我不知道他们什么时候再来。
四、用法注意点: 1.在时间和条件状语从句中,主句为过去将来时时,从句常用一般过去时来表示过去将来时。例如: He said he wuld cme t see yu when he had ( 实义动词,have的过去式 ) time. 他说他有时间就来看望你。 2.“wuld+动词原形”可表示过去习惯性的动作。此时,不管什么人称,都可用wuld。 When he was a child he wuld get up early. 他年幼时,总是很早起床。
1. They wanted t knw when yu_____ the drawing . A. will finish B. wuld be finished C. wuld finish D. will be finish 2. Sally said she______ in a few days. A. will cme B. wuld cme C. had cme D. came
in + 一段时间: 用于将来时态时,表示在这段时间以后。
---Did yur brther knw it_____? ---N, I dn’t think s. Because he didn’t take an umbrella with him. A. wuld rain B. rained C. was raining D. was ging t rain 4. He thught I ____ wrk early tday. A. will B. am ging t get t C. gt t D. was ging t get t
过将的基本形式: wuld/ shuld +动词原形过将的其他形式: 1.was/were+ging t+动词原形 2.was/were+t+动词原形 3.was/were abut+动词原形 4.过去进行时(一般多为动作概念较强的动词,如 g,cme, leave,start, pen,begin 等)也可用于表示将来。
概念: 表示过去正在发生的动作结构: be (was,were) + ding标志语: 1) at this time last night, at 8:00 yesterday2) when… , while…3) frm seven t nine4) yesterday, last year, yesterday mrning
1)在过去某一时间正在进行的动作。What were yu ding at 8:30 yesterday evening ?2)一个动作发生时,另一个动作正在进行。I was sleeping when it started t rain. 3)过去进行时(一般多为动作概念较强的动词,如 g,cme, leave,start, pen,begin , arrive 等)也可用于表示过去将来。 I didn't knw when they were cming again. 我不知道他们什么时候再来。 He was leaving the first week in June and staying until September.
1. His uncle_____ all night last Mnday . A. wrks B. was wrking C. wrked D. has wrked 2. He______ his bicycle when it began t rain. A. was riding B. is riding C. has ridden D. rides
When 从句的用法:主延续从短暂 (如题2)主短暂从延续主短暂从短暂
While 从句的用法: 主延续从延续表对比,“然而,而”
概念: 表示将要发生的动作标志语:1) tmrrw, tday, tnight 2) next spring / week / mnth / year3) during this term 4) first, next5) when I grw up….
1.will+动词原形 (I /we shall)2.be ging t+动词原形3.be+t d 表示计划,责任,约定或命令4. be abut t d sth 表示正要做…,马上要做...(不能与表示将来时间的状语连用)5.be+v-ing6.一般现在时表将来
1.will+v原形 与 shall+v原形 shall用于第一人称,常被will 所代替。 will 在陈述句中用于各人称,在争求意见时常用于第二人称。1)表示一个将来的动作或状态,“要…,会…”She will g t the park tmrrw.2)表示不以人的意志为转移的自然发展的事。Spring will cme again.Tmrrw will be Sunday.3) will+v 有时表示说话是临时决定或打算。 --- My car wn’t start. ---Dn’t wrry, I will cme and give it a push.
4) will+v 的特殊用法: 祈使句+ and/r+将来时(will)
努力工作否则你就会失败。Wrk hard r yu will fail.努力工作你就会成功。Wrk hard and yu will succeed.
2. be ging t +不定式,表示将来。 主语的意图,即将做某事。 What are yu ging t d tmrrw?b. 计划,安排要发生的事。 The play is ging t be prduced next mnth.c. 有迹象要发生的事 Lk at the dark cluds, there is ging t be a strm.
3.be t d ①表按计划或安排即将发生的动作②表示约定,责任,命令,或注定要发生的动作。③官方计划或决定(常见于报纸或广播)He and I are t meet at the railway statin tmrrw. Yu are nt t be back late.If nt watered, the plants are t die.The president is t speak n TV tnight.
4. be abut t d 表示正要做…,马上要做... (不能与表示将来的时间的状语连用) was /were abut t d … when… 正要…突然发生…英语晚会即将开始。The English Evening Party is abut t begin.我正要出去,这时下起了雨.I was abut t g ut when it began t rain.
5. be +v-ing g, cme, leave, start, arrive, stay, fly, land, take ff 等动词可用现在进行时表示安排和计划或即将发生的动作。我们明天动身去青岛.We’re leaving fr Qingda.
6.表示与生日,日历,课时安排或交通时刻表有关的动作(一种规律) ,用一般现在时表示将来时态常用于转移动词如:begin, cme , leave, g, arrive, start, stp, return, pen, clse… The evening class begins at 19:00. 火车两点出发.The train starts at tw.
注:在时间或条件状语从句中,从句用一般现在时表示将来时:when, as sn as, befre, nce, if , unless, even if, in case If yu cme this mrning, we will have a meeting. When I graduate, I will g t the cuntryside.
1. be ging t 与 will 的区别 用于条件句时, be ging t 表将来 will 表意愿1). If yu are ging t make a jurney, yu'd better getready fr it as sn as pssible.2). Nw if yu will take ff yur clthes, we will fit the new clthes n yu in frnt f the mirrr. 2. be t 与 be ging t 的区别 be t 表示客观安排或受人指示而做某事。be ging t 表示主观的打算或计划。I am t play ftball tmrrw afternn. (客观安排)I’m ging t play ftball tmrrw afternn. (主观安排)
—What wuld yu d if it _______ tmrrw ? —We have t carry it n, since we’ve gt everything ready. A. rain B. rains C. will rain D. is raining
2. —What are yu ging t d this afternn? —I am ging t the cinema with sme friends. The film _____quite early, s we ____ t the bkstre after that. A. finished; are ging B. finished; g C. finishes; are ging D. finishes; g
3. My yunger brther ____be 15 years ld next year. A. is ging t B. will C. is t D. shuld
4. — Srry, I frgt t pst the letter fr yu. — Never mind, _____ pst it myself tnight. A. I’m ging t B. I prefer t C. I’ll D. I’d rather
5. —Write t me when yu get hme. — ____________. A. I must B. I shuld C. I will D. I can
6. Let’s keep t the pint r we _____ any decisins. A. will never reach B. have never reached C. never reach D. never reached
7. If he _____ t cllege, he _____ a lt mre. A. will g; will learn B. will g; is ging t learn C. ges; will learn D. ges; is ging t learn
人教版初中中考英语语法系列---名词课件: 这是一份人教版初中中考英语语法系列---名词课件,共26页。PPT课件主要包含了名 词,名词所有格,所有格的构成方式, 名词所有格练习,Exercises等内容,欢迎下载使用。
人教版初中英语语法系列---冠词课件: 这是一份人教版初中英语语法系列---冠词课件,共44页。PPT课件主要包含了英语中的一些语法概念,音的概念,音素音标,音的分类,词的概念,十大词性,冠 词,冠词的分类,冠词口诀,不定冠词口诀等内容,欢迎下载使用。
人教版初中英语语法系列---非谓语动词课件: 这是一份人教版初中英语语法系列---非谓语动词课件,共60页。PPT课件主要包含了非谓语动词,with,about,动词不定式, 动 名 词,动名词的特点,① 抽象② 习惯性,Participle等内容,欢迎下载使用。













